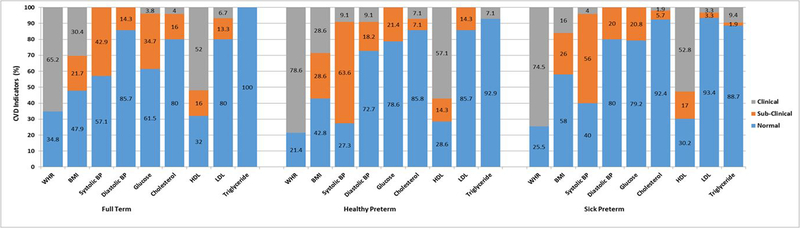
Figure 2.
Clinical and sub-clinical cardiovascular risk indicators at age 23 by neonatal group for females only.
Note. CVD=Cardiovascular Indicators; WHR=Waist-Hip Ratio; BMI=Body Mass Index; BP=Blood Pressure; HDL=High Density Lipoprotein; LDL=Low Density Lipoprotein.
Clinical & sub-clinical classifications. Body fat percentage (i.e., BMI) was classified as low (underweight; <18.5), normal (healthy weight; 18.5–24.9), high (overweight; 25–29.9), and very high (obese/morbidly obese; >30) and WHR greater than 1.0 was classified as high risk. Prehypertensive systolic BP sub-clinical cut-off was 120–139 mmHg and hypertensive systolic BP clinical cut-off was >140mmHg. (American Heart Association, 2015) Prehypertensive diastolic BP sub-clinical cut-off was 80–89mmHg and hypertensive diastolic BP clinical cut-off was >90mmHg. Clinical and sub-clinical classifications for lipid profiles were: total cholesterol was normal ≤199 mg/dL, borderline 200–239 mg/dL, high ≥240 mg/dL; HDL ranges were high (good) ≥60 mg/dL, borderline 41–59 mg/dL, low (bad) ≤40 mg/dL; LDL ranges were optimal/near optimal ≤129 mg/dL, borderline 130–159 mg/dL, high/very high ≥160 mg/dL; and triglycerides ranges were normal ≤149 mg/dL, borderline 150–199 mg/dL, high/very high ≥200 mg/dL.