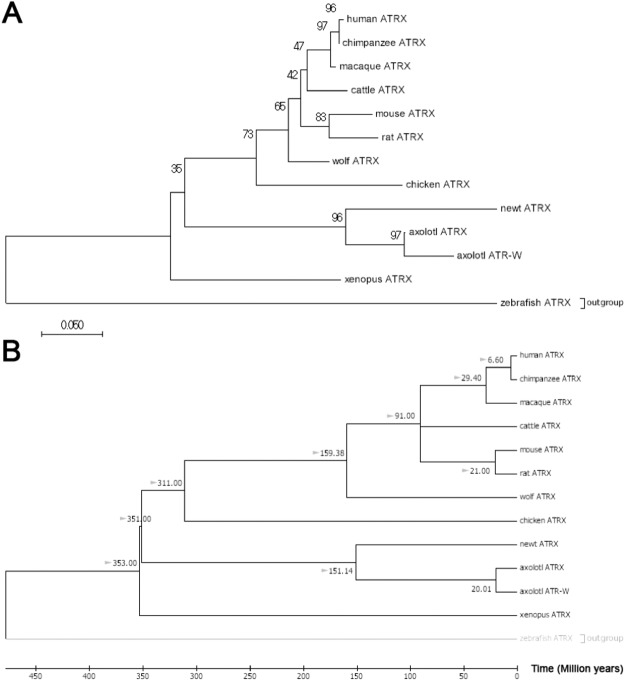
Figure 6.
Neighbor-Joining trees for vertebrate ATRX with bootstrap and divergence time estimations. (A) Evolutionary relationships among ATRX homologs were inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method87. The bootstrap consensus tree inferred from 10000 replicates is taken to represent the evolutionary history of the taxa analyzed88. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (10000 replicates) are shown next to the branches88. Evolutionary distances were computed using the Maximum Composite Likelihood method89 and are in the units of the number of base substitutions per site. The analysis involved 13 nucleotide sequences. Codon positions included were 1st + 2nd + 3rd + Noncoding. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated resulting in the inclusion of 251 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA784. The newt represents sequence from Notophthalmus viridescens. (B) A time-scaled phylogenetic tree inferred using the Reltime method90 and estimates of branch lengths inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method as in A87. The tree was computed using 10 calibration constraints. Divergence times estimated by Timetree were added manually and are marked with gray arrows49. This tree indicates that the duplication event giving rise to ATRW in axolotl may have occurred ~20MYA.