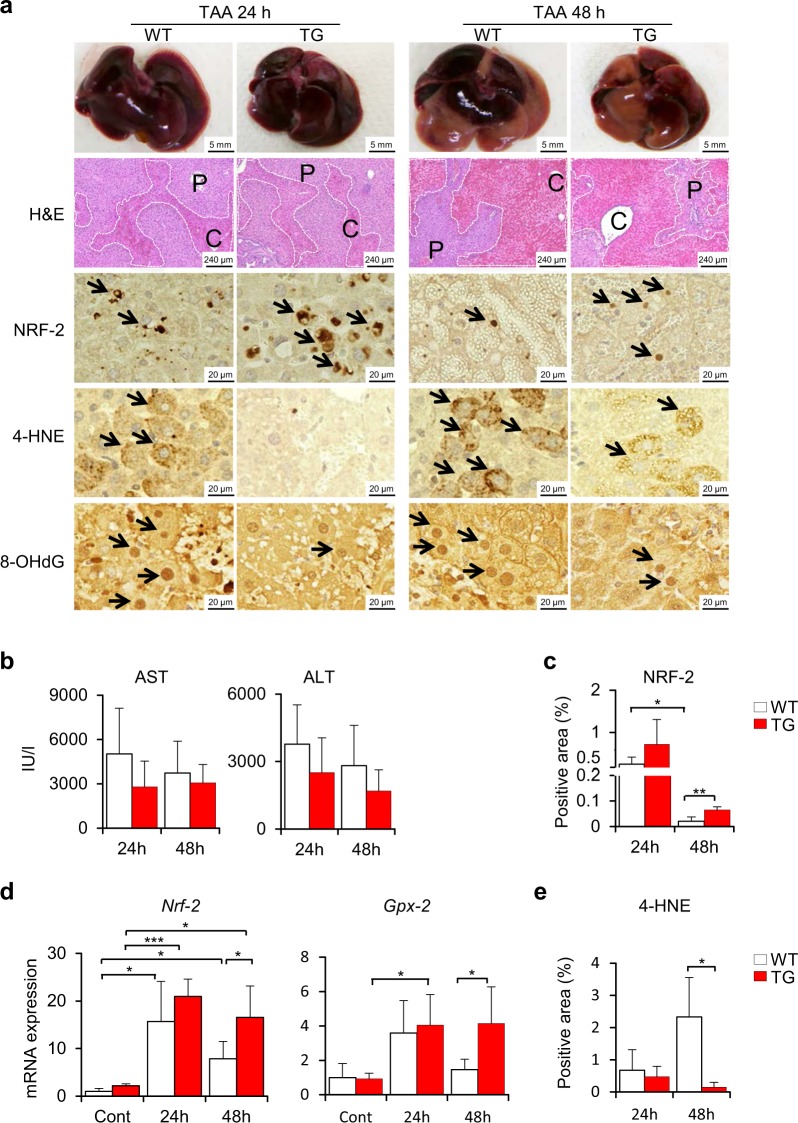
Figure 3.
Suppression of oxidative stress in Cygb-TG mice challenged with a single dose of TAA. (a) Macroscopic and microscopic view of liver injuries in wild- type (WT) and Cygb-TG mice (TG) after 24 hours (24 h) or 48 hours (48 h) of exposure to a single dose of TAA. Representative images of gross appearance, H&E staining, and immunohistochemistry staining for erythroid 2–related factor 2 (NRF-2), 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE), and 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG). P, portal vein; C, central vein. Dashed line shows the haemorrhagic area. (b) Plasma levels of AST and ALT were measured. (c) Percentages of NRF-2-positive areas of liver sections were quantified. (d) Transcription of Nrf-2 - the antioxidative signalling pathway and its downstream component - glutathione peroxidase 2 (Gpx-2). (e) Percentages of 4-HNE-positive areas per 20 random micro fields in liver sections at 400x magnification were quantified. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 5), *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01.