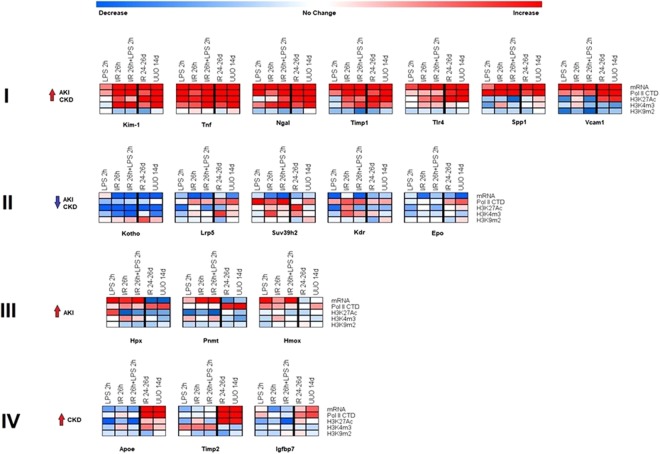
Figure 4.
Integrated transcriptional and epigenetic analysis of selected sets of renal injury genes from AKI and CKD models. RT-qPCR RNA analysis. Total RNA from injured kidneys and controls kidneys (n = 6 mice for each model) was used in RT reactions with oligo-dT primers. cDNA was used in real time qPCR with gene specific primers (same as Figs 1–3). Transcript levels were normalized to ribosomal protein mRNA L32 (same as Figs 1–3) ChIP-qPCR analysis. Tissue fragments from injured and control (contralateral) kidneys (n = 6 mice for each injury model) were crosslinked and sonicated. Sheared chromatin was analyzed in Matrix ChIP-qPCR using antibodies to RNA polymerase II (Pol II) and antibodies to permissive (H3K27Ac, H3K4m3) and repressive (H3K9m2) marks. ChIP signals were normalized to input. Data represents log2 transformed ratios of means from injured kidneys over controls. Shown are genes whose expression was: (I) upregulated in both AKI and CKD; there was agreement between the increased in mRNA, Pol II and the permissive H3K27Ac levels. For most of these genes there was also increased in permissive H3K4m3 modification but decreased H3K9m3 repressive mark; (II) downregulated in both AKI and CKD;Pol II levels were either increased or in case of Klotho slightly decreased with decreased permissive but increased repressive modifications at this gene. (III) upregulated in AKI but not in CKD; Pol II levels in AKI were only moderately elevated and the epigenetic changes were small and (IV) upregulated in CKD but not in AKI; there was corresponding increase in Pol II and permissive H3K27Ac.