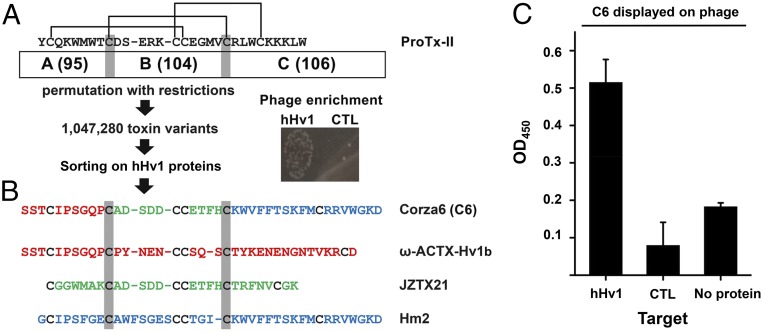
Fig. 1.
C6 is isolated from an ICK scaffold, phage-display library. ICK scaffold phage library construction, hHv1 protein purification, phage preparation, and sorting are described in Materials and Methods. (A) Library design and phage sorting. A total of 110 ICK toxin sequences was aligned on conserved Cys residues (indicated by the gray highlighting) to define three domains that correspond to ProTx-II residues Tyr1–Thr8, Asp10–Val20, and Arg22–Trp30, respectively. Black lines indicate the arrangement of disulfide bridges. This yields 95, 104, and 106 unique A, B, and C domains, respectively (SI Appendix, Table S1), that combine to produce a calculated library diversity of ∼1 million for all natural and novel ABC peptides. After five rounds of selection on hHv1 protein, phage enrichment was observed compared with the streptavidin control. (B) Corza6 (C6) is a novel toxin isolated from the library screening. DNA sequencing revealed that C6 toxin phage had been enriched after phage sorting. C6 composed of residues present in three natural parental spider toxins, ω-ACTX-Hv1b (red), JZTX21 (green), and Hm2 (blue). (C) ELISA shows C6 phage binds to hHv1 protein but not control protein streptavidin and ELISA plate (no protein). The 96-well plates coated with or without target protein were incubated with C6 phage (1010/well). Data are mean ± SD for three wells.