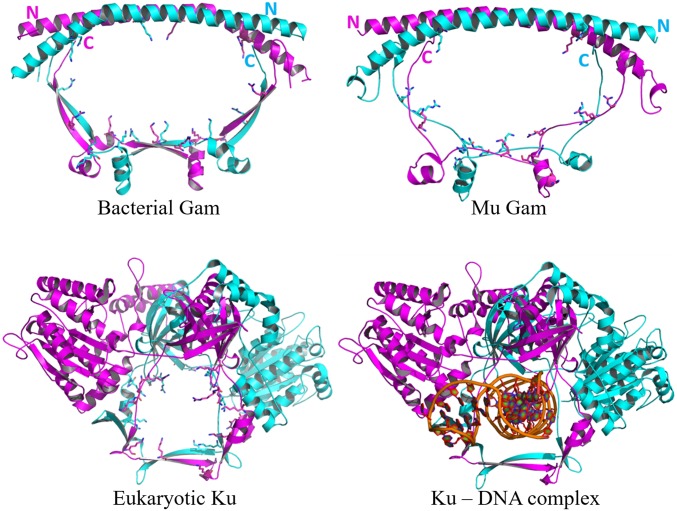
Fig. 1.
Structural comparison of eukaryotic Ku, bacterial Gam, and MuGam. (Upper Left) Crystal structure of DvGam homodimer (PDB ID code 2P2U). (Upper Right) A homology model of phage MuGam dimer (see Methods). (Lower Left) Crystal structure of a eukaryotic Ku heterodimer (PDB ID code 1JEQ). (Lower Right) Ku in presence of dsDNA (PDB ID code 1JEY). Positively charged amino acid residues projecting into the central DNA-binding cavity for Ku, and into the equivalent space for Gam, are represented as sticks. The central cavity in DvGam is twice as wide as that in Ku (36 Å × 65 Å vs. 30 Å × 24 Å).