Fig. 2.
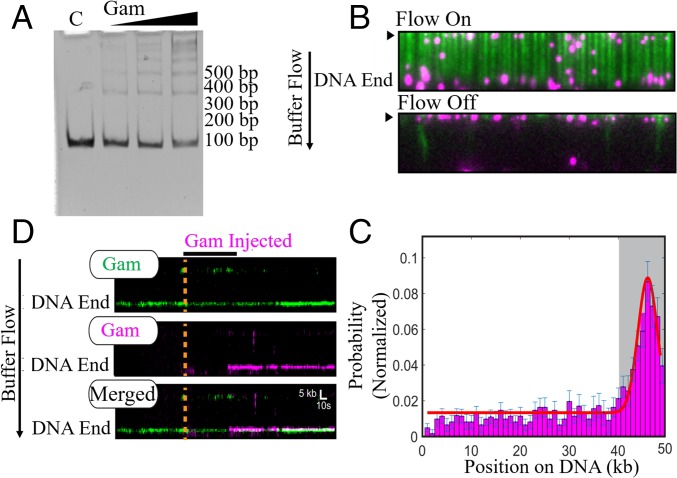
MuGam is located predominantly at DNA ends. (A) EMSA assay. Linear dsDNA (100 bp) was incubated with increasing amounts of tagless Gam, electrophoresed on a 5% native acrylamide gel, and visualized by ethidium bromide (EtBr) staining. C, DNA alone control. Position of size markers is indicated on the right. (B) Fluorescent FLAG-Gam (magenta) binds λ−DNA organized at microfabricated barriers (green, labeled with YOYO1 dye). Turning off buffer flow retracts both Gam and DNA to the barriers (black arrow), indicating that Gam is on the DNA. (C) A binding distribution of Gam along the DNA shows a strong preference for DNA ends. Gray region indicates the experimental uncertainty in defining the DNA end. Error bars were determined by bootstrap analysis. Red line denotes the Gaussian fit. (D) Multiple FLAG-Gam molecules can stack on a free DNA end, as indicated by colocalization of green- and magenta-labeled Gams on a single DNA molecule. Position of the Gam-bound DNA end is indicated. Orange dashed line and black horizontal bar indicate when the magenta Gam was injected into the flow cell. See Methods for experimental details.