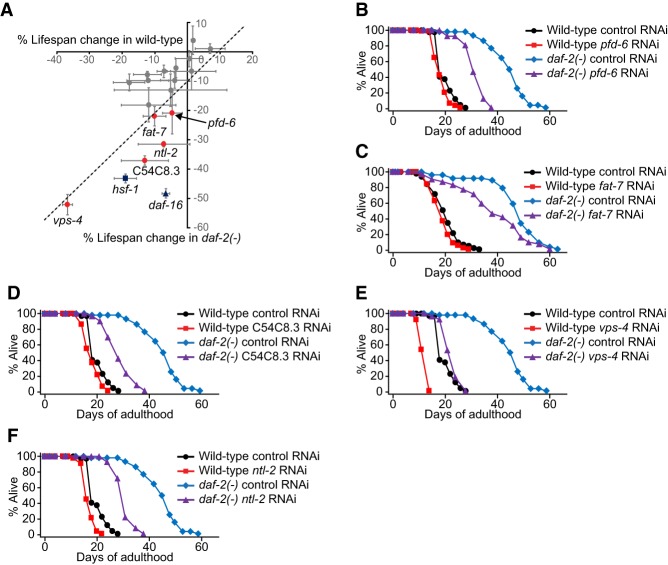
Figure 1.
Five hsf-1(sy441) sterility enhancer RNAi clones decrease the longevity of daf-2 mutants. (A) The graph shows percentage changes in the average life span of wild-type (X-axis) and daf-2(e1370) [daf-2(−); Y-axis] animals treated with each of 17 RNAi clones obtained from the primary screen. Each circle, square, or triangle indicates an average value of two different sets of life spans. A dashed line indicates an arbitrary cutoff showing RNAi clones that have 10% more life span-decreasing effects on daf-2 mutants than on wild type. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (SEM) of two independent experiments. Worms were treated with RNAi only during adulthood to exclude the possibility that RNAi clones may affect the health of the animals during development. hsf-1 RNAi and daf-16 RNAi clones were used as positive controls. (B–F) pfd-6 RNAi (B), fat-7 RNAi (C), C54C8.3 RNAi (D), vps-4 RNAi (E), and ntl-2 RNAi (F) substantially decreased the life spans of daf-2 mutants while having little effect on that of wild-type animals. For pfd-6, we confirmed the increased sterility caused by pfd-6 RNAi in hsf-1 mutants using solid plates (Supplemental Fig. S1E). See Supplemental Table S2 for statistical analysis and additional repeats.