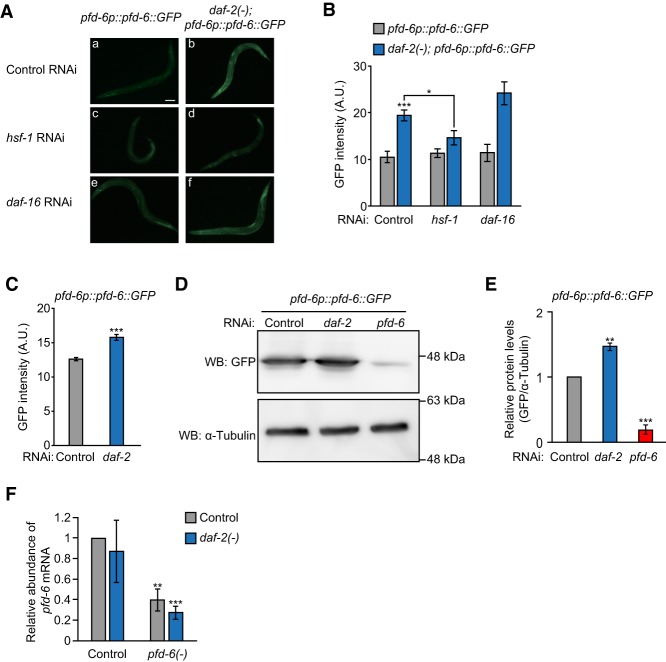
Figure 5.
HSF-1 increases the levels of PFD-6. (A) Mutations in daf-2 increased PFD-6 levels, which were decreased by hsf-1 RNAi but not by daf-16 RNAi. Bar, 100 µm. The following animals that expressed an extrachromosomal array of pfd-6::GFP were used: IJ570 (yhEx134[pfd-6p::pfd-6::GFP; odr-1p::RFP]) and IJ810 {daf-2(e1370); yhEx134[pfd-6p::pfd-6::GFP, odr-1p::RFP]}. (B) Quantification of A. n > 15 from two independent experiments. (C) GFP levels in integrated pfd-6::GFP transgenic animals (IJ1249: yhIs74[pfd-6p::pfd-6::GFP; odr-1p::RFP]) were examined. n > 32 from three independent experiments. (D) Western blot assays were performed using the IJ1249 strain. A representative blot is shown from three repeats that displayed consistent results. α-Tubulin was used as a loading control. (WB) Western blot. (E) Quantification of D. (F) mRNA levels of pfd-6 in wild-type, daf-2(e1370) [daf-2(−)], pfd-6(gk493446, RNAi) [pfd-6(−)], and pfd-6(−); daf-2(−) animals were measured by using quantitative RT–PCR. n = 3. Error bars represent SEM. (*) P < 0.05; (**) P < 0.01; (***) P < 0.001, two-tailed Student's t-test.