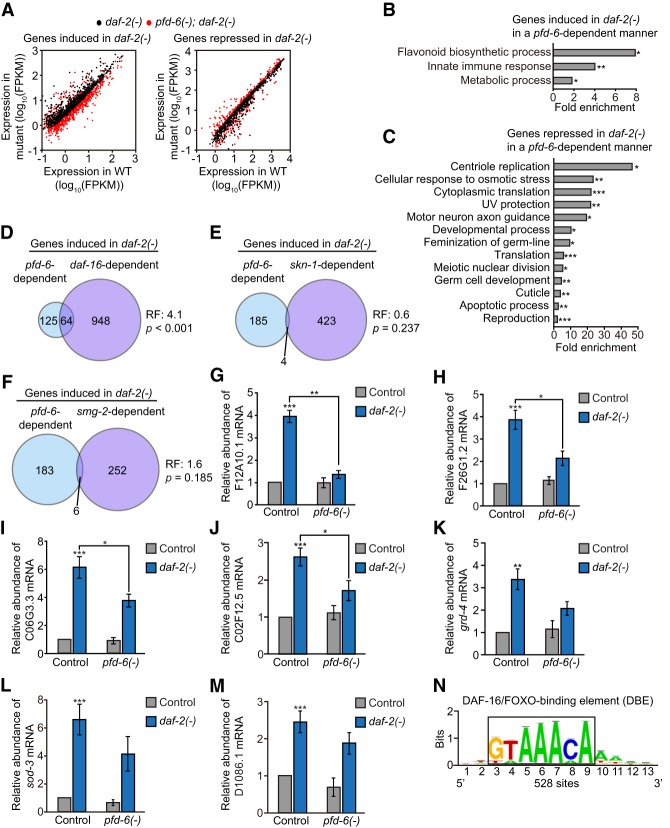
Figure 6.
PFD-6 up-regulates a large subset of DAF-16 target genes in daf-2 mutants. (A) Scatter plots show the comparison of gene expression between wild-type and daf-2(e1370) [daf-2(−)] or wild-type and pfd-6(gk493446, RNAi); daf-2(e1370) [pfd-6(−); daf-2(−)] animals. Black dots indicate gene expression in daf-2 mutants compared with wild type, whose levels were significantly increased (fold change >1.50; P < 0.05; left) or decreased (fold change <0.67; P < 0.05; right). Red dots indicate expression levels in pfd-6; daf-2 mutants compared with wild type. See Supplemental Table S8 for the list of up-regulated or down-regulated genes in daf-2 mutants compared with wild-type or pfd-6; daf-2 double mutants. (B,C) Overrepresented GO terms of up-regulated (B) or down-regulated (C) genes that are shown in A. (*) P < 0.05; (**) P < 0.01; (***) P < 0.001. (D–F) Venn diagrams indicate overlapping genes whose expression was increased by daf-2 mutations in a pfd-6- and daf-16-dependent (Riedel et al. 2013) (D), pfd-6- and skn-1-dependent (Ewald et al. 2015) (E), or pfd-6- and smg-2-dependent (Son et al. 2017) (F) manner. Fold change > 1.5. P < 0.05. (RF) Representation factor. P-values for the overlaps of Venn diagrams were calculated using the hypergeometric probability test. (G–M) qRT–PCR results showing mRNA levels of DAF-16 target genes F12A10.1 (G), F26G1.2 (H), C06G3.3 (I), C02F12.5 (J), grd-4 (K), sod-3 (L), and D1086.1 (M). n > 4. Error bars represent SEM. (*) P < 0.05; (**) P < 0.01; (***) P < 0.001, two-tailed Student's t-test. (N) Motif analysis was performed by using 800-base-pair (bp) upstream sequences of pfd-6-dependent genes that were up-regulated in daf-2 mutants. Fold change > 1.5. P < 0.05. See Supplemental Figure S6, O and P, for other enriched motifs.