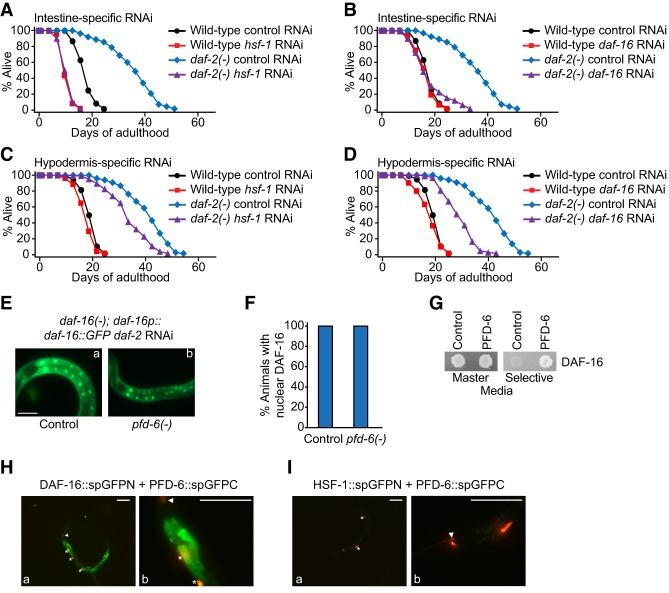
Figure 7.
PFD-6 binds and up-regulates DAF-16/FOXO in daf-2(−) mutants. (A–D) Intestine-specific (A,B) or hypodermis-specific (C,D) hsf-1 or daf-16 RNAi decreased the longevity of daf-2(e1370) [daf-2(−)] mutants. See Supplemental Table S6 for statistical analysis and additional repeats. (E) daf-2 RNAi-induced nuclear localization of DAF-16::GFP was not affected by pfd-6 mutations. (F) Quantification of E. n > 18 from three independent experiments. Bars, 100 µm. (G) Yeast two-hybrid assays showed the direct interaction between PFD-6 and DAF-16. (H) GFP N-terminal domain-fused DAF-16 isoform a (DAF-16::spGFPN) bound GFP C-terminal domain-fused PFD-6 (PFD-6::spGFPC). See Supplemental Figure S7J for experimental results using daf-2 RNAi-treated animals. (I) HSF-1::spGFPN did not bind PFD-6::spGFPC. Triangles indicate odr-1p::RFP, a coinjection marker for DAF-16::spGFPN and HSF-1::spGFPN. Asterisks indicate unc-122p::RFP, a coinjection marker for PFD-6::spGFPC.