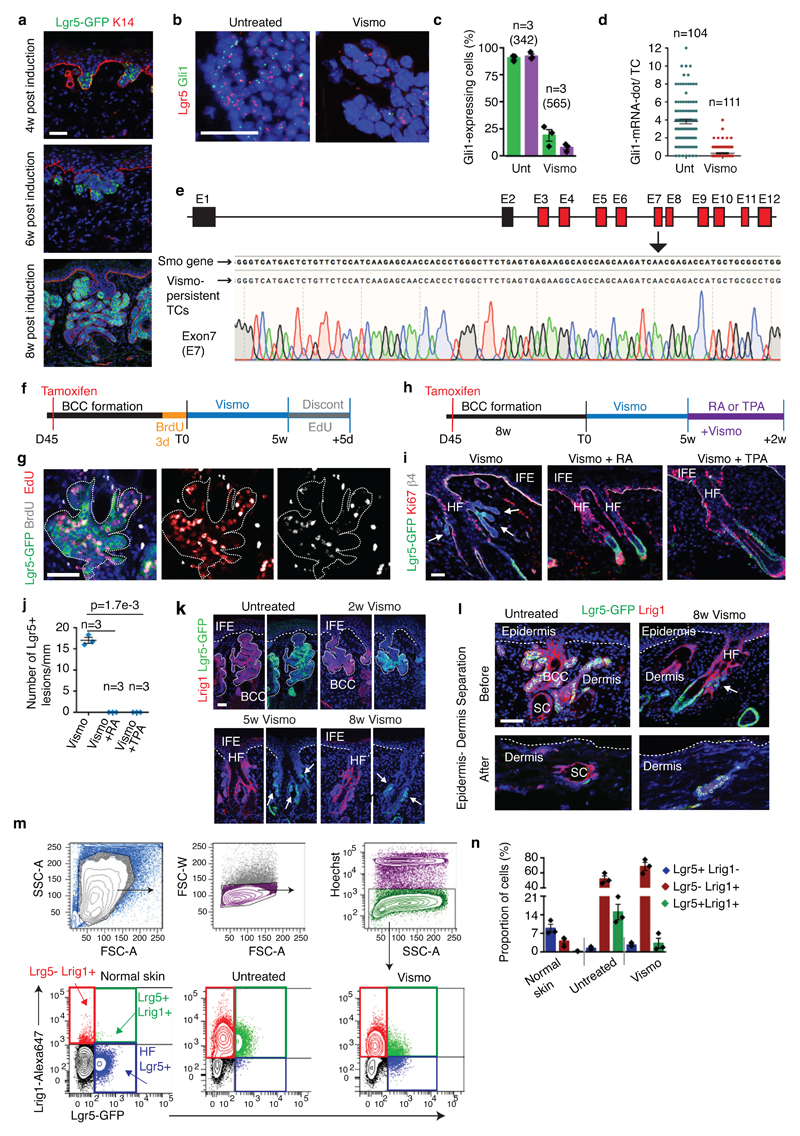
Extended Data Fig 2. Vismodegib-persistent lesions express Lgr5 in mice.
(a) Immunostaining for GFP and K14 at different time points post tamoxifen administration in the K14CreER/Ptch1cKO/Lgr5-DTR-GFP mice. (b) In situ hybridization for Lgr5 and Gli1 in untreated and treated TCs in SmoM2 mice. (c) Percentage of TCs (Lgr5+ and Lgr5-) that express Gli1 in SmoM2 mice (n=3 mice, total number of cells analysed indicated in parenthesis). Mean +/- s.e.m. (d) Distribution of the number of Gli1-mRNA-dot per TC with and without treatment in SmoM2 mice (n=104 and 111 total TCs from 3 mouse per condition and time point). Mean +/- s.e.m. (e) Representation of the mouse Smo gene, in red the exons (E) in which genetic mutations have been described6,7 (upper panel). Results from the sequencing of the exon 7 from vismodegib-persistent lesions obtained by pooling drug-persistent cells from 3 mice, showing absence of genetic mutations in the exon analysed (lower panel). See Source data for sequencing results of exons 3-12. (f) Protocol for BrdU/EdU double labelling studies in BCC followed by vismodegib administration and discontinuation in the Ptch1cKO-induced BCCs. (g) Immunostaining for GFP, BrdU and EdU mice following 5 days of vismodegib discontinuation in Ptch1cKO/Lgr5-DTR-GFP-derived BCCs. (h) Protocol for vismodegib and RA or TPA treatment. (i) Immunostaining for GFP, Ki67 and β4 in the back skin of Ptch1cKO/Lgr5-DTR-GFP animals treated with vismodegib and RA or TPA. (j) Quantification of the number of Lgr5+ tumorigenic lesions per length of skin upon vismodegib and vismodegib with RA or TPA treatment (n= 3 Ptch1cKO/Lgr5-DTR-GFP mice, 3mm of skin analysed per mouse). Two-sided t-test. (k)Immunostaining for GFP and Lrig1 in untreated and treated Ptch1cKO/Lgr5-DTR-GFP mice. (l)Immunostaining for GFP and Lrig1 in untreated and 8 weeks vismodegib treated mice before and after enzymatic and physical separation of epidermis from dermis in Ptch1cKO/Lgr5-DTR-GFP mice. Note that HF co-expressing Lgr5 and Lrig1 and the sebaceous cysts remained in the dermal fraction whereas the BCCs were isolated with the epidermal fraction, indicating that the normal HF did not significantly contaminate the FACS isolated TCs.(m) Cell sorting strategy to isolate Lgr5+Lrig1-, Lgr5+Lrig1+ and Lgr5-Lrig1+ in normal skin and in Ptch1cKO/Lgr5-DTR-GFP-derived BCCs before and after vismodegib administration. Forward scatter (FSC) and side scatter (SSC) were performed to exclude cell debris and doublets. Living cells were selected by Hoechst dye exclusion. Finally, the different Lgr5 and Lrig1 cell populations were isolated by FACS sorting. A: area; W: width. (n) Proportion of cells presenting Lgr5-GFP and Lrig1 expression determined by FACS (n=3 independent experiments per condition). Histograms represent the mean and error bars de s.e.m. These experiments indicate that Lrig1 can be used to discriminate between Lgr5+ cells coming from the HFSC or lower HF (Lgr5+Lrig1-) from BCC cells (Lgr5+Lrig1+). Three independent experiments per condition were analysed showing similar results in a, k and l. Hoechst nuclear staining in blue; scale bars, 50 μm in a, i, k and l and 25 μm in b. Dashed line delineates basal lamina separating IFE from the dermis. Dotted line delineates BCC. Arrow indicates vismodegib-persistent lesion.