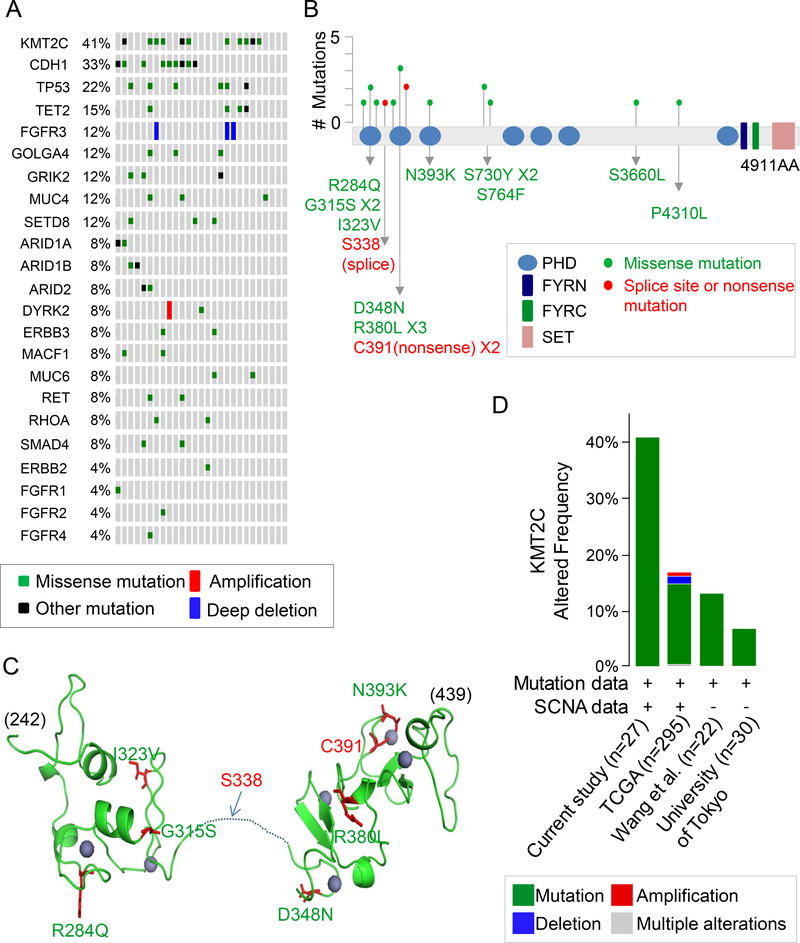
Figure 1. KMT2C mutations in diffuse type gastric adenocarcinoma.
(A) List of commonly mutated genes following whole exome sequencing of 27 diffuse type GA samples. (B) Location and type of KMT2C mutations. The protein domains are as follows: blue, plant homeotic (PHD) domains; navy,PHD-like zinc-binding domainPHD-like zinc-binding domain FY-rich N-terminal (FYRN) domain; green, FYR C-terminal (FYRC) domain; pink, SET domain. A red dot indicates a splice site or nonsense mutation; a green dot indicates a missense mutation. (C) Predicted 3-dimensional model of PHD domains zinc finger (PDB ID: 2YSM and 5ERC) generated using PyMol (DeLano Scientific, CA). Homology modeling was made with SWISS model (https://swissmodel.expasy.org). Positions of the mutations are shown (green, missense mutation; red, splice site or nonsense mutation). Zinc is shown as purple spheres. Most mutations are located in the residues associated with zinc coordination. (D) Frequency of KMT2C alterations in GA samples in this study compared to previous genomic studies from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) (7); Wang et al.(9); and University of Tokyo (10), along with types of alterations. The image was generated using the cBioPortal (http://www.cbioportal.org)