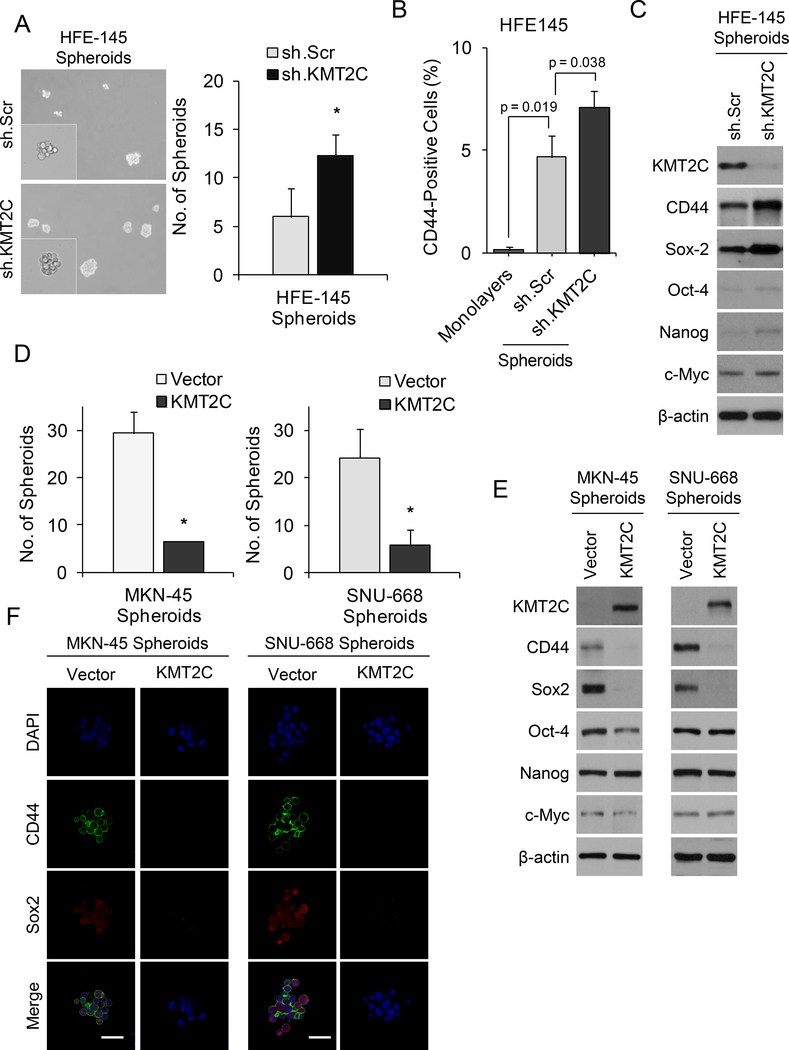
Figure 5. Role of KMT2C in cancer stem-like cell phenotypes.
(A) Photos and graph of spheroid formation assay for HFE-145 cells transduced with KMT2C shRNA (sh.KMT2C) or scrambled control shRNA (sh.Scr). (B) Graph showing percent of CD44 positive cells by FACS analysis for HFE-145 monolayers cells, spheroid cells transduced with sh.Scr, and spheroid cells transduced with sh.KMT2C. (C) Western blot demonstrating levels of KMT2C, the gastric CSC marker, CD44, and self-renewal proteins for Sox2, Oct-4, Nanog, and c-Myc in HFE-145 cells transduced with sh.KMT2C or sh.Scr. (D) Spheroid formation assays for MKN-45 and SNU-668 cells transduced with a KMT2C expression vector (KMT2C) or a control vector (Vector). (E) Western blot demonstrating levels of KMT2C, the gastric CSC marker, CD44, and self-renewal proteins for Sox2, Oct-4, Nanog, and c-Myc in MKN-45 and SNU-668 cells transduced with a control vector or with a KMT2C expression vector. (F) Immunofluorescence photos for DAPI, CD44, and Sox2 of MKN-45 and SNU-668 cells transduced with a KMT2C expression vector or control vector. Scale bar 50 μm. Bars represent standard deviation. *p<0.05 compared to control.