Figure 2.
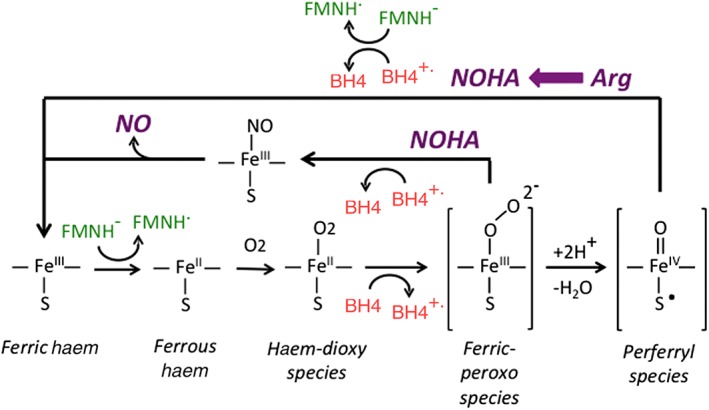
NOS O2 activation steps and the accompanying BH4 redox transitions that occur during the Arg and NOHA oxidation reactions. The catalysis starts with the ferric enzyme being reduced by an electron from the reductase domain (FMNH−). This allows the haem to bind O2 and form the haem‐dioxy species, which is then reduced by BH4 to form the reactive haem‐oxy species that react either with Arg or with NOHA as indicated. After Arg is oxidized to NOHA, the reductase domain provides an electron to reduce the NOS‐bound BH4 radical back to BH4 and, in doing so, resets the ferric enzyme for catalysis of NOHA oxidation. During the NOHA reaction, the BH4 radical that forms receives an electron from a NOS reaction/product species, and this allows generation of the enzyme ferric haem‐NO species that releases NO.
