Figure 2.
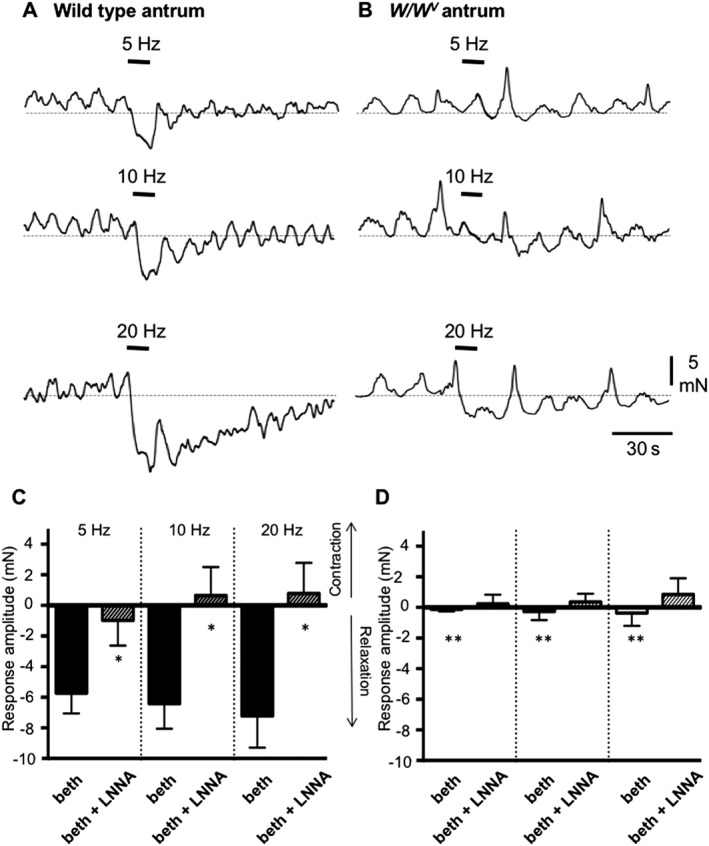
Antral responses to vagal nerve stimulation in wild‐type and W/W v mice. Contractions of wild‐type and W/W V antral muscles were measured in response to electrical vagal stimulation (EVS; 5, 10 and 20 Hz; delivered during periods denoted by black bars). Muscles were pretreated with bethanechol (3 μM). (A) EVS elicited relaxation of wild‐type muscles, and the amplitude of the relaxation increased with stimulus frequency. (B) EVS caused relaxation of W/W V muscles, as well, but the responses were of much smaller amplitude than in wild‐type muscles. (C, D) Summary of experiments showing average responses to EVS in wild‐type (n = 15) and W/W V (n = 8) antral muscles before and in the presence of L‐NNA (100 μM). Data in W/W V muscles were tested against responses under same conditions in wild‐type muscles: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. Redrawn from Beckett et al. (2017).
