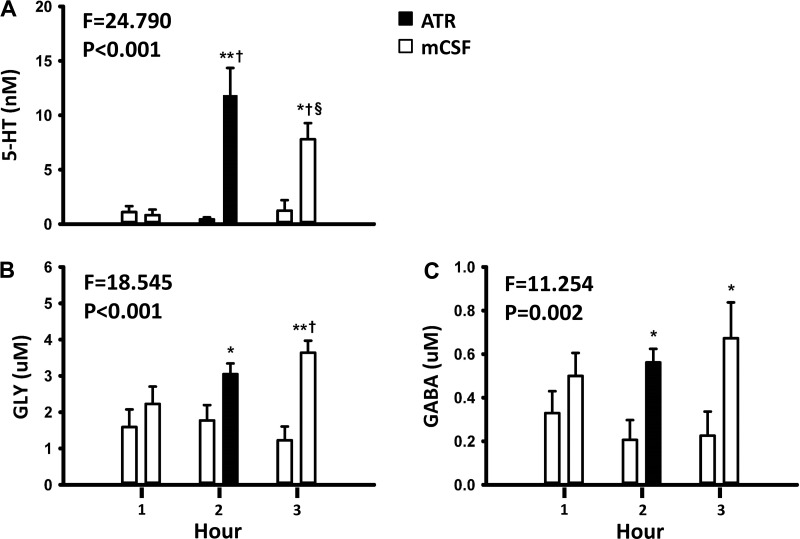
Fig. 3.
Dialysis of the muscarinic receptor antagonist atropine (ATR) into the ventral respiratory column (VRC) elicits apparent compensatory changes in other neuromodulators. Compared with dialysis of mock cerebral spinal fluid (mCSF) alone, the concentrations of serotonin (5-HT; A), glycine (GLY; B), γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA; C) were increased (P < 0.05) in the effluent mCSF during daytime unilateral dialysis into the VRC of 50 mM atropine. The x-axis is hour of dialysis. The 1st bar for each hour is when mCSF was dialyzed all 3 h while the 2nd bar is when 50 mM atropine was dialyzed during the 2nd hour (closed bar). F and P values are from two-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, significant difference between treatments; **P < 0.001 between groups; †P < 0.001 comparisons with hour 1; §P < 0. 001, comparisons with hour 2 by by post hoc analysis (Holm-Sidak).