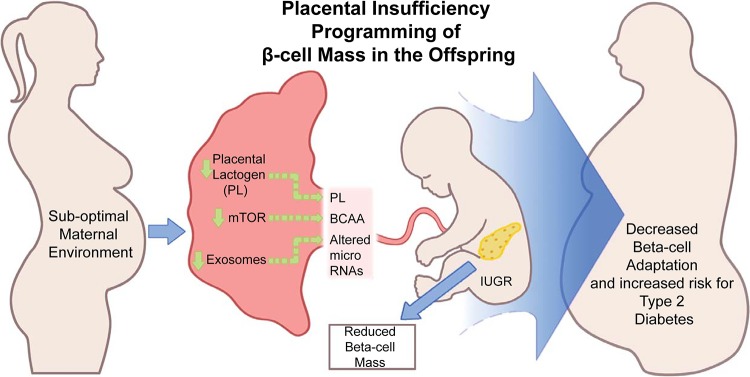
Fig. 1.
Placental insufficiency programming of β-cell mass in the offspring. Fetal intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) is a result of changes in suboptimal maternal intrauterine environment, which influences placental function. This includes several integrated factors, including but not limited to reduced activity of mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathways, specific hormones such as placental lactogen levels, and exosomal content (i.e., microRNAs). All of these factors may contribute to fetal IUGR and the development of pancreatic β-cell mass in the fetus. BCAA, branched chain amino acid.