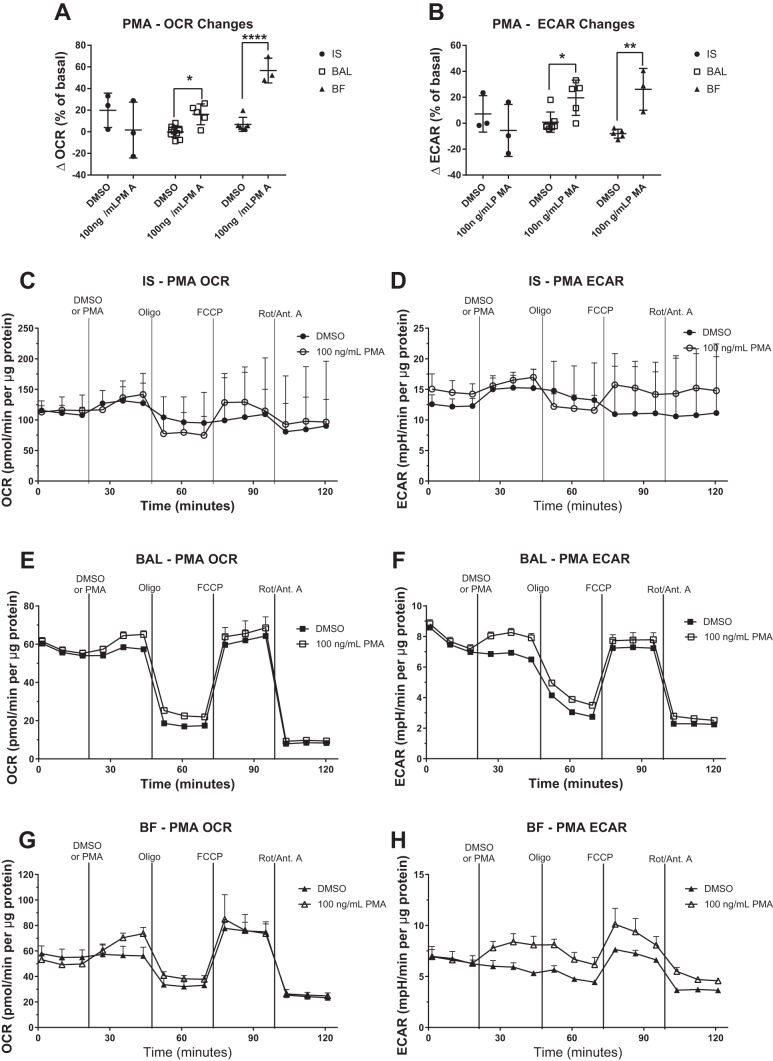
Fig. 8.
Activation of protein kinase C induces bronchoalveolar and bronchial fraction (BF) macrophage oxygen consumption rate (OCR) and extracellular acidification rate (ECAR). Cells collected by induced sputum (IS), bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), and BF were stimulated with the protein kinase C activator PMA, and bioenergetic changes were monitored by extracellular flux analysis. OCR and ECAR were measured at basal conditions, following the addition of 100 ng/ml PMA and in response to a mitochondrial stress test [oligomycin (Oligo), FCCP, rotenone/antimycin A (Rot/Ant. A)]. Data are expressed as the means. OCR (A) and ECAR (B) changes in response to PMA addition over a 24-min exposure are shown as a percentage of the basal OCR or ECAR. Representative OCR and ECAR graphs are shown for IS (C and D), BAL (E and F), and BF (G and H), n ≥ 3, means + SD. OCR and ECAR data were normalized to total protein content in the sample. *P < 0.05 and ****P < 0.001 between means of DMSO control and PMA groups.