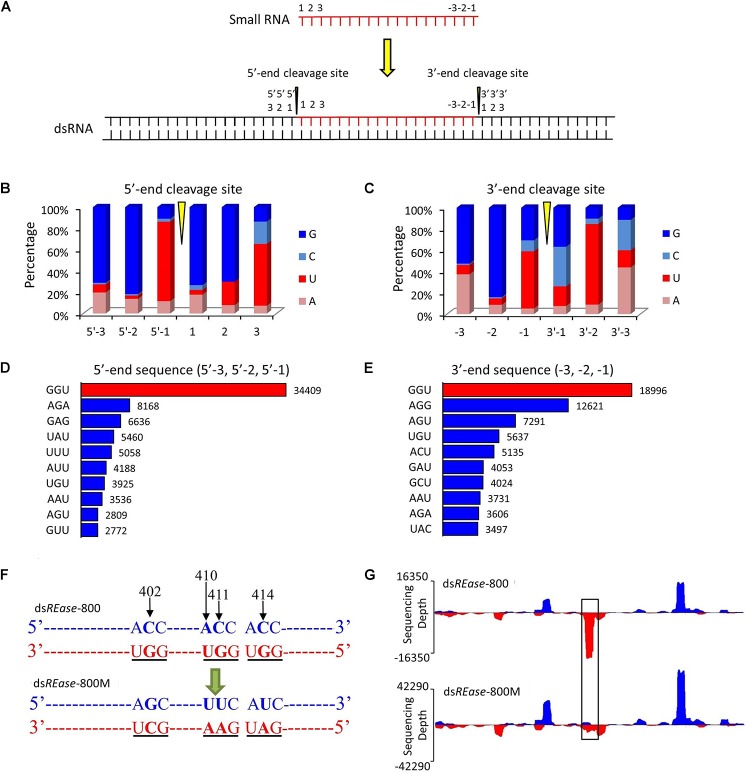
FIGURE 2.
GGU is a major cleavage site for in vivo dsRNA-processing into small RNAs. (A) Outline of the dsRNA cleavage site analysis. Three nucleotide bases on the 5′- and 3′-ends of a small RNA were labeled as 1, 2, and 3, and -3, -2, and -1, respectively. When one small RNA was mapped on the reference dsRNA sequence, the small RNA cleavage site was revealed. Three nucleotide bases before the 5′-end’s cleavage site were labeled as 5′-3, 5′-2, and 5′-1. Similarly, three nucleotide bases after the small RNA’s 3′-end cleavage site were named as 3′-1, 3′-2, and 3′-3. (B,C) Nucleotide components of 5′- and 3′-end cleavage sites of the top 0.1% of small RNAs that match on the reference sequence. (D,E) Three nucleotides components of the top ten 5′- and 3′- end cleavage sites of the top 1.0% of 19–25 nt small RNAs. The nucleotide components of the 5′-end sequence represent the information on sites of 5′-3, 5′-2, and 5′-1, and those of 3′-end sequence represent the information on sites of -3, -2, and -1. (F) GGU site’s mutant design. One small RNA peak representing an area with three GGU cleavage sites was selected in dsREase-800. The site-specific mutations were produced by PCR. The nucleotide site 402, 410, 411, and 414 on the sense chain were mutant from CACC to GUUU. Thus, the three GGU sites on the antisense chain were changed to GCU, GAA, and GAU. (G) The small RNA peak was lost when the GGU site was mutant. Four hours later injection with 10 μg dsREase-800 with three GGU sites or 10 μg dsREase-800M with GGU mutation, total RNA was extracted from the fifth instar Asian corn borer larvae. Then, small RNAs were isolated and sequenced (sequence data are listed in Supplementary Tables 2–5). The 19–25 nt long small RNAs that matched on the reference sequences were used for graphing.