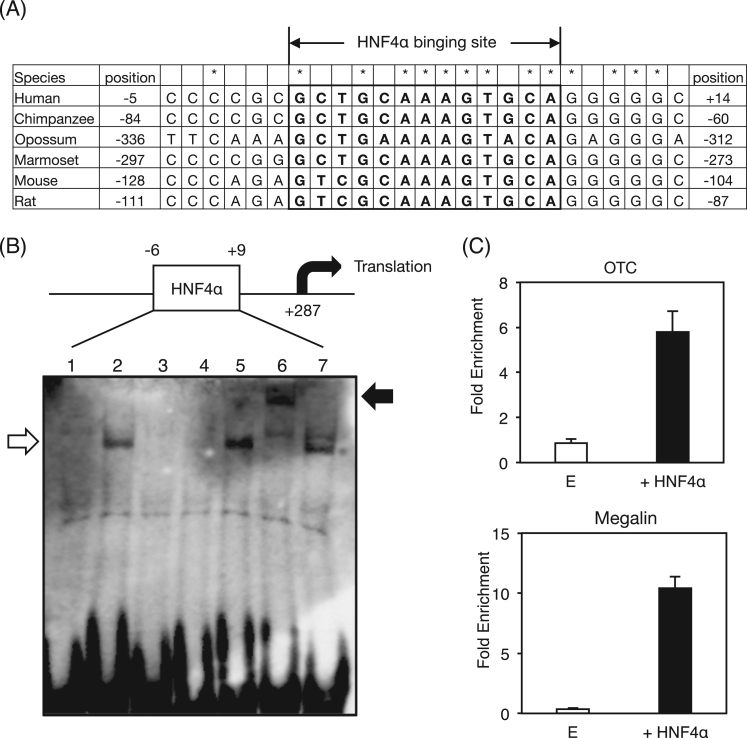
Fig. 3.
Binding of HNF4α to the megalin promoter. (A) Sequence alignment of the megalin promoter in human, chimpanzee, opossum, marmoset, mouse, and rat. Predicted HNF4α⎕binding site is enclosed in box. Completely conserved nucleotides among the species are shown as asterisk. (B) Electrophoresis mobility shift assay. The megalin probe carrying the HNF4α binding site at 6-/+9 was incubated without or with nuclear extracts from HNF4α-transfected HEK293T cells (lanes 1 and 2). The megalin probe with the nuclear extracts was incubated with the nuclear extracts in the presence of excess amount of the unlabeled Otc competitor (lane 3), the unlabeled megalin competitor (lane 4), and the unlabeled megalin competitor containing the mutated HNF4α⎕binding site (lane 5). For supershift analysis, anti-HNF4α and anti-PPARβ antibodies were added (lanes 6 and 7). (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation using empty vector or HNF4α expression vector-transfected HEK293T cells were performed with anti-HNF4α antibody and normal goat IgG. The regions with or without the HNF4α binding sites in the human OTC and megalin gene were amplified. The data from real-time PCR was normalized relative to the input and expressed as fold-enrichment over the data from IgG control. Data are mean ± S.D.