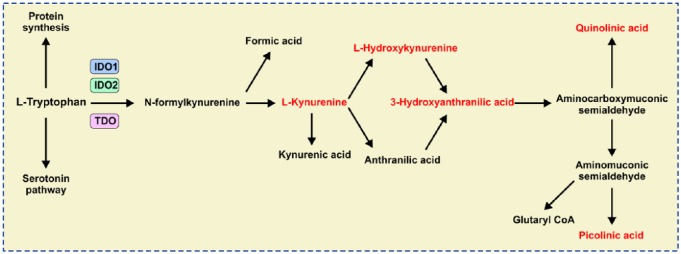
Figure 1.
The kynurenine (KYN) pathway of tryptophan (TRP) metabolism.
L-TRP is metabolized in three separate biochemical pathways enabling protein and serotonin synthesis. The KYN-dependent pathway begins when IDO1/IDO2/TDO catalyze L-TRP into N-formylkynurenine. N-formylkynurenine is then transformed into L-KYN and formic acid by kynurenine formamidase. L-KYN is converted to anthranilic acid by kynureninase or L-hydroxykynurenine by kynurenine hydroxylase. Hydroxylation of anthranilic acid results in generation of L-hydroxykynurenine. Kynureninase converts L-hydroxykynurenine to 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid that is further metabolized by hydroxyanthranilate dioxygenase to aminocarboxymuconic semialdehyde. Quinolinic acid and aminomuconic semialdehyde are generated from the semialdehyde. Aminomuconic semialdehyde is then converted to picolinic acid or glutaryl-coenzyme A (CoA) that is metabolized in the tricarbonic acid cycle and terminal oxidation.
IDO1, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; TDO, tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase.