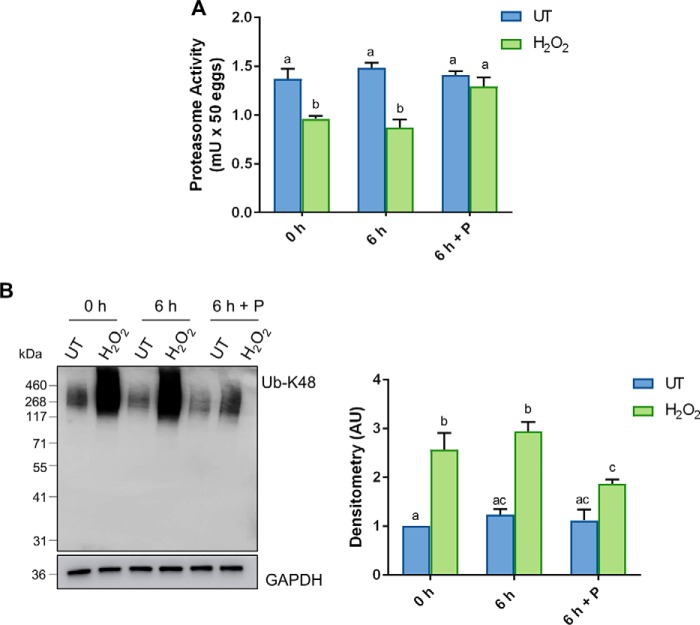
Figure 7.
Penicillamine restores the proteasome activity of the oxidatively-damaged oocyte. GV oocytes were treated with 35 μm H2O2 (H2O2) for 1 h to induce oxidative stress and were then immediately processed (0 h) or incubated for an additional 6 h in either the absence (6 h) or the presence of penicillamine (100 μm) (6 h + P), prior to IVM for 16 h. MII oocytes were identified by the presence of a polar body. A, decrease in proteasome activity was observed after H2O2 (ANOVA; p = 0.0087), with penicillamine treatment after H2O2 exposure able to restore the effect of H2O2 on proteasome activity (ANOVA; p = 0.0462). One unit of proteasome activity is defined as the amount of proteasome that generates 1.0 nmol of the fluorescently tagged AMC per min at 37 °C. B, increase in ubiquitin in oxidatively-stressed oocytes was detected via immunoblotting with anti-UB-K48 antibodies, with penicillamine after H2O2 exposure able to significantly decrease ubiquitination (ANOVA; p = 0.0365). Immunoblots were performed in biological and technical triplicate using 100 oocytes per lane pooled from a minimum of three animals. Whole lanes were used for densitometry analysis. Immunoblots were stripped and re-probed with anti-GAPDH antibodies as a loading control. Data are presented as mean of three replicates ± S.E. AU, arbitrary units.