Figure 10.
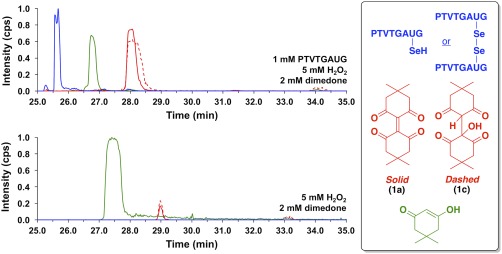
Extracted ion chromatograms monitoring the elution of species with m/z values of 751.8 and 752.8 (blue), 277.2 (red, solid), 295.0 (red, dashed), and 141.0 (green) after (top) the reaction of 1 mM peptide H‐PTVTGAUG‐OH, 5 mM H2O2, and 2 mM dimedone in 100 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4 for 25 min, or (bottom) the reaction of 5 mM H2O2 and 2 mM dimedone in 100 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4 for 25 min. These m/z values correspond to peptide H‐PTVTGAUG‐OH as the selenol (m/z 752.8), peptide H‐PTVTGAUG‐OH as the diselenide (m/z 751.8), dimeric dimedone species 1a (m/z 277.2), the water adduct of 1 (1c; m/z 295.0), and dimedone (m/z = 141.0), respectively. The top panel demonstrates that 1a can be used as a chemical footprint for the detection of Sec‐seleninic acid under conditions of oxidative stress (5× molar excess of H2O2 in this case). The bottom panel shows a control experiment in which the Sec‐containing peptide H‐PTVTGAUG‐OH is absent, but dimedone (2 mM) and H2O2 (5 mM) are present.
