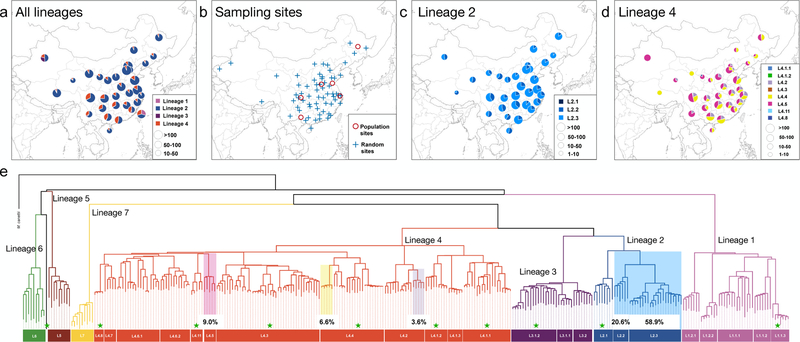
Fig. 1. Genotyping results of countrywide collected MTBC strains in China.
(a) The prevalence of different MTBC lineages in 32 provinces based on spoligotyping data from 16,221 isolates collected throughout China. (b) The 76 county sites from which MTBC isolates were sampled for this study: “population sites” are counties where MTBC isolates were collected through exhaustive sampling from 2009–2010, and “random sites” are counties where MTBC isolates were randomly sampled in 2007. SNP typing results of L2 strains (c) and L4 strains (d) show the relative proportion of each sublineage in each province. (e) Phylogeny of 301 MTBC isolates reflecting diversity found worldwide. Branches are colored according to the convention described in Comas et al 2010. Sublineages found commonly in China are highlighted, with a notation of their prevalence. Sublineages that were rarely encountered in China are marked with green pentacles; the remaining unmarked sublineages were not identified in China.