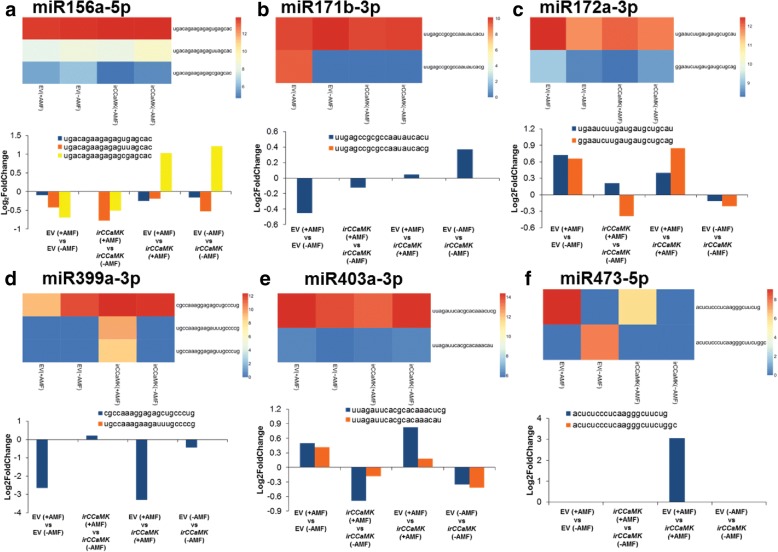
Fig. 6.
Sequence variants observed for conserved miRNAs in EV and irCCaMK plants demonstrate strong differences in abundance depending on the genotype and AMF inoculation. Each miRNA is depicted by two panels, a heatmap showing the normalized RPM values for each sequence variant in the four conditions, and a bar-chart representing the differential abundances of these sequence variants in the four comparisons (a-f). Three sequences with one nucleotide difference towards the 3′ end were observed for miR156a-5p (a). These variants have originated from different genomic locations with different precursor sequences. One of the variants was highly abundant (> 9000) in all four conditions (blue color in heatmap), whereas the other sequence variants were far less abundant (< 100 RPM values). For miR171b-3p (b) two sequence variants were found which originated from different genomic loci. One of the variants was only captured in EV (+AMF) with > 400 RPM values. For miR172a-3p (c) 2 sequence variants were found, both originating from different genomic loci. All three sequence variants of miR399a-3p (d) were captured in irCCaMK (+AMF), while only one sequence variant was found in EV and non-inoculated plants. MiR403a-3p (e) and miR473-5p (f) were sequenced with two different sequences, originating from the same chromosome