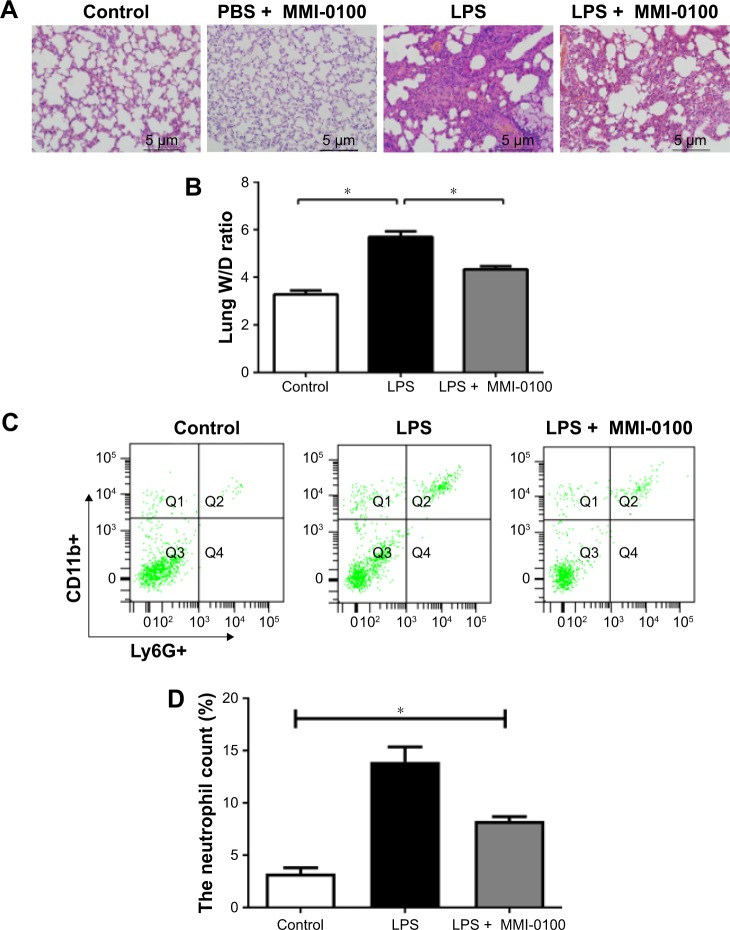
Figure 1.
The damage caused by LPS in the mouse lungs.
Notes: The mice were killed 24 hours after administration of LPS or PBS. (A) The upper lobes of the right lung of each mouse were harvested, and the degree of acute lung injury was assessed by H&E staining (×200). (B) The middle lobes of the right lung were collected, weighed quickly to record the wet weight, and then dried in an oven at 85°C for 24 hours to be able to record the dry weight. The W/Ds were calculated. (C, D) The number of neutrophils in each mouse lung was determined using a flow cytometer counting cells stained with antibodies against CD11b+ and Ly6G+. The values presented are the mean ± SEM (n=15 in each group). Comparisons were made by one-way ANOVA, and the results were representative of three independent experiments. *P<0.05.
Abbreviations: LPS, lipopolysaccharides; W/Ds, wet/dry weight ratios.