Extended Data Figure 5. LILRB4 promotes infiltration of AML cells.
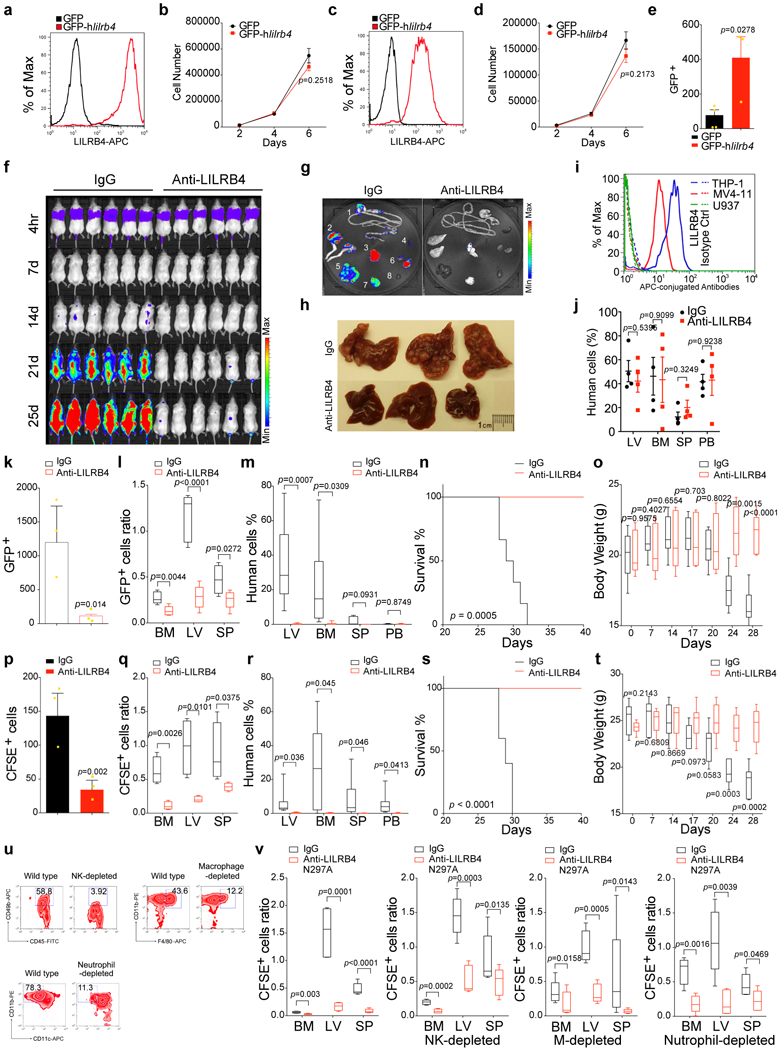
a and c, Examination of LILRB4 expression on mouse AML cells, C1498 (a) or WEHI-3 (c) that stably express lilrb4. b and d, Forced expression of LILRB4 did not affect cell proliferation of mouse AML cells, C1498 (b, n=3 biologically independent samples with mean and s.e.m.) or WEHI-3 (d, n=3 biologically independent samples with mean and s.e.m.). e, Forced expression of human LILRB4 promoted transendothelial migration of mouse AML WEHI-3 cells (n=3 biologically independent samples with mean and s.e.m.). f, NSG mice (n=6 mice) were injected with 1×106 THP-1 cells followed immediately by IgG or anti-LILRB4 antibody treatment and were monitored by bioluminescence imaging. g-h, Anti-LILRB4 antibodies decreased AML cells infiltration into internal organs. Mice were sacrificed at 21 days for ex vivo bioluminescence imaging of internal organs after transplantation of 1×106 luciferase-expressed THP-1 cells. Images of luminescence flux (radiance) from representative mice are shown (g). 1: GI tract; 2: legs; 3: lung; 4: spleen; 5: liver; 6: kidneys; 7: brain; 8: heart. Infiltrated leukemia cells formed tumor nodules in liver (h). i-j, Anti-LILRB4 antibodies did not have effect on LILRB4-negative cancer cells. LILRB4 is expressed on THP-1 and MV4–11 human AML cells but not on U937 cells as analyzed by flow cytometry (i). Isotype IgG was used as control. NSG mice were injected with U937 human AML cells, which do not express LILRB4, and then treated with anti-LILRB4 antibodies (j). IgG served as control antibodies. Mice were sacrificed at day 25 post-transplant for analysis of LV, BM, SP, and PB by flow cytometry. The presence of human AML cells was detected by anti-human CD45 antibody staining (n=4 mice with mean and s.e.m.). k-t, Anti-LILRB4 antibodies decreased infiltration of THP-1 (k-o) or MV4–11 (p-t) human AML cells. Comparison of transendothelial migration abilities of GFP-expressing THP-1 (k) or CFSE-labeled MV4–11 (p) cells after treatment with anti-LILRB4 antibody or IgG control in a transwell assay (n=3 biologically independent samples with mean and s.e.m.). Comparison of the homing abilities of CFSE-labeled MV4–11 cells (5×106 per mouse) that were injected into NSG mice followed immediately by IgG or anti-LILRB4 antibody treatment at 20 hr post-injection (n=5 mice). Numbers of leukemia cells (GFP+ in l or CFSE+ in q) in LV, SP, and BM normalized to that in PB as determined by flow cytometry are shown. NSG mice were injected with 1×106 THP-1 or MV4–11 cells followed immediately by IgG or anti-LILRB4 antibody treatment (n=6 mice for THP-1 or 5 mice for MV4–11 xenografts). Shown are percentages of MV4–11 cells (stained with anti-human CD45) as determined by flow cytometry in indicated organs at day 21 post-transplant (m and r), overall survival (n and s), and body weights as a function of time (o and t). u, Targeted immune cell populations were depleted in NSG mice. Representative flow cytometry plots demonstrating successful reduction of NK cell (CD45+CD49b+), macrophage (CD11b+F4/80+), and neutrophil (CD11b+CD11c-) frequency in NSG mice depleted of the respective immune cell subtype by treatment with anti-asialo GM1 antibodies, clodronate liposomes, and anti-Ly6G antibodies, respectively, compared to non-depleted (wild-type) NSG mice. v, CFSE-labeled MV4–11 cells (5×106 per mouse) were injected into NSG mice in that respective innate immune cells were depleted, followed immediately by IgG or anti-LILRB4-N297A antibody treatment (n=5 mice). Numbers of leukemia cells (CFSE positive) in LV, SP, and BM normalized to that in PB at 20 hr post-injection are shown. (a, c, i and u) These experiments were repeated independently three times with similar results. See Methods for definition of box plot elements in l-m, o, q-r, t and v. All p values (except of n and s from long-rank test) were from two-tailed student t-test.
