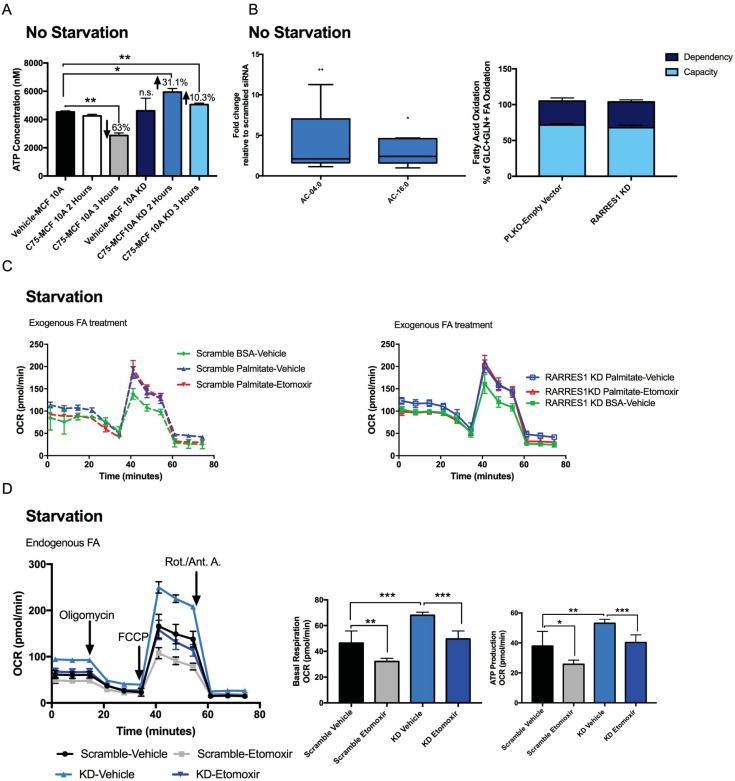
Fig 3. RARRES1 depletion regulates fatty acid oxidation.
(A) ATP content was quantified in transient RARRES1 KD MCF 10A cells and scrambled siRNA MCF 10A cells after 2 and 3 hours of 40 μg/mL C75 treatment. (B) All detected Acylcarnitines, AC-4:0 and AC-16:0, were quantified and validated in the non-targeted LC-MS results of RARRES1 siRNA transfected MCF 10A cells (S2A Fig). The fold change was normalized to scrambled siRNA transfected MCF 10A cells. Fatty acid oxidation rate in RARRES1-depleted cells was measured in nutrient rich media. FAO dependency and flexibility of the cells were calculated. Initial inhibition of FAO by etomoxir measures how dependent the cells are on that particular fuel source to meet the energy demand. Using a combination of glycolytic, glutaminolytic and FAO inhibitors, the cells' capacity and flexibility in meeting energy demand were calculated in terms of oxygen consumption rate. (C) Fatty acid oxidation dependent mitochondrial respiration was quantified and the effects of exogenous fatty acids (palmitate treatment) on FAO-dependent OCR in RARRES1-depleted and scrambled siRNA MCF 10A cells in glucose and serum starved media. (D) MCF 10A were starved and treated with etomoxir to measure fatty acid oxidation rate dependent on endogenous fatty acids. Scrambled siRNA and transient RARRES1 siRNA were measured and compared. Basal respiration and ATP production were quantified.