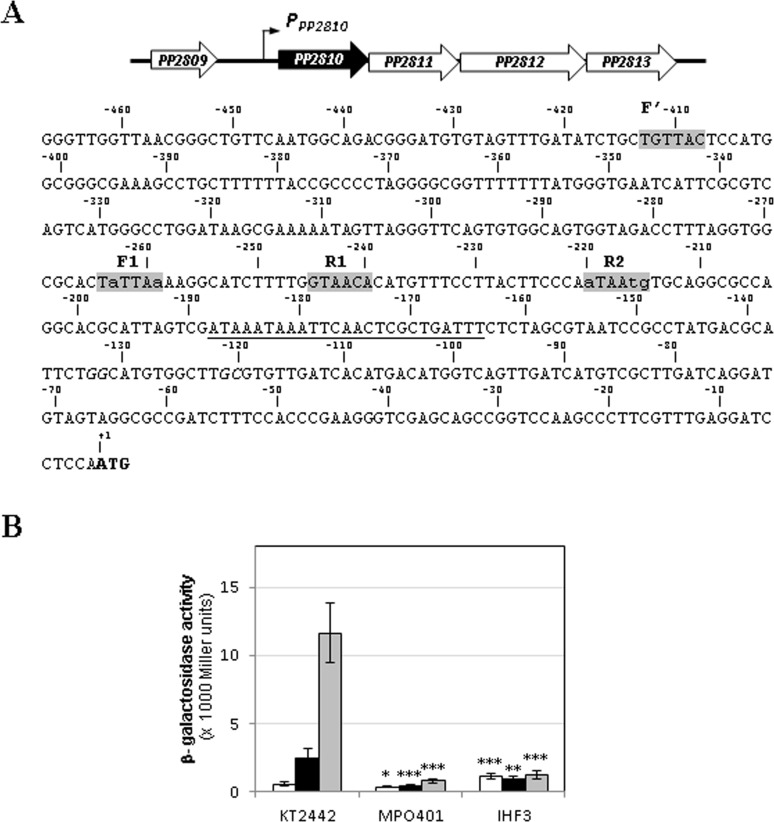
Fig 2.
(A) Genomic context and sequence of operon PP2810-PP2813. Genomic context of PP2810 scheme in Pseudomonas putida along with its promoter sequence from the position -467 with respect to the initiation of translation (ATG, in bold). Sequences in grey correspond to CbrB binding subsites; the underlined sequence represents the σN-dependent promoter sequence (GG-N10-GC) and the boxed sequence represents the putative IHF binding site. (B) In vivo expression from the P. putida PP2810 promoter. Expression was measured as β-galactosidase activity of the PP2810::lacZ transcriptional fusions (plasmid pMPO420) of cultures of the KT2442 wild-type, the MPO401 (ΔcbrB) and IHF3 mutant strains, grown in LB (white bars) or in minimal medium containing succinate (black) or oxaloacetate (grey bars) as carbon sources. The values are the average of at least three independent assays. The error bars indicate the standard deviation of the means. Stars designate p-values for the Student's t-test for unpaired samples not assuming equal variance and are referred to the wild type strain. *: p<0.05; **: p<0.01; ***:p<0.005.