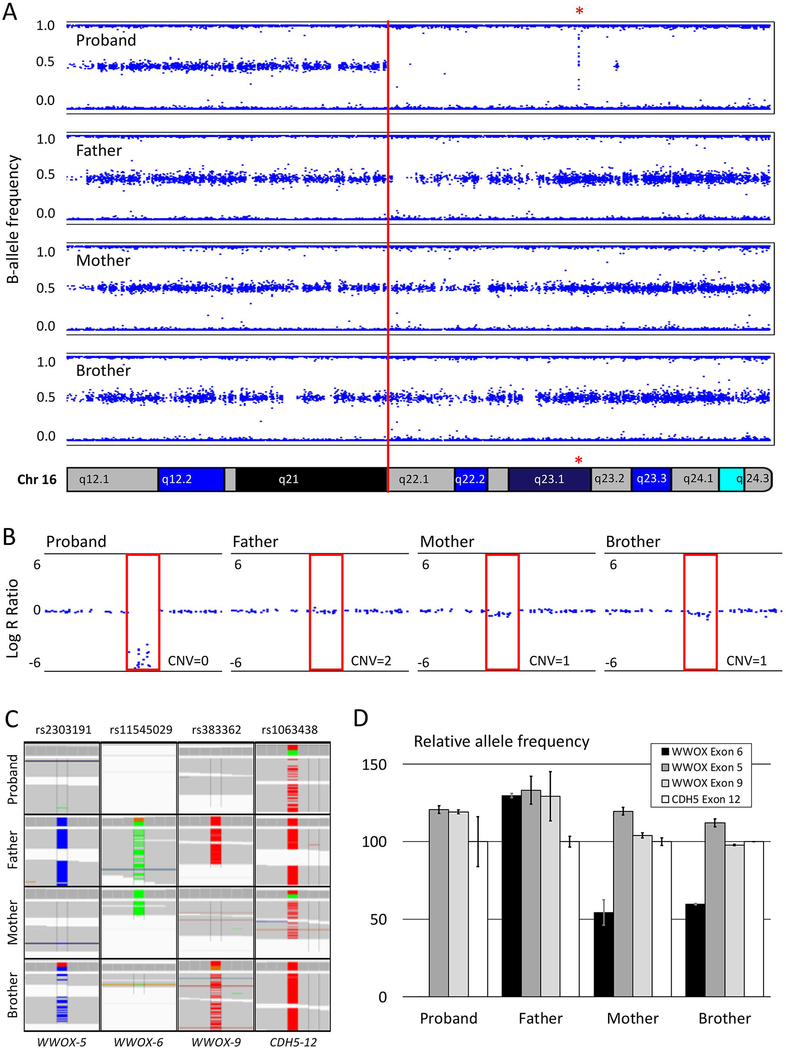
Figure 1: Genetic analysis of the homozygous region on chromosome 16.
A. B-allele frequency plot of a single-nucleotide-polymorphism (SNP)-array showing a large stretch of homozygosity from 16q22.1–16q24.3 present in the affected proband but not in the unaffected family members. The red asterisk indicates the location of the exon 6 deletion in WWOX. B. The Log-R ratio on the SNP-array shows the copy number variation (CNV) at WWOX exon 6. The proband has a CNV of 0 and the mother and brother have a CNV of 1, whereas the father has both alleles at this location. C. Three SNPs in and near WWOX exon 5, 6 and 9 reveal non-Mendelian inheritance for the proband, who consistently inherited only the variant from her mother. The SNP in exon 12 of CDH5, located at 16q21 shows normal Mendelian inheritance for the proband. D. Relative mRNA expression reflecting allele frequencies for the three non-Mendelian SNPs in WWOX determined by digital droplet PCR. No loss of alleles for WWOX exons 5 and 9 compared to exon 12 of CDH5 confirmed the bi-allelic deletion of exon 6 observed in our proband and the mono-allelic deletion in the mother and the brother.