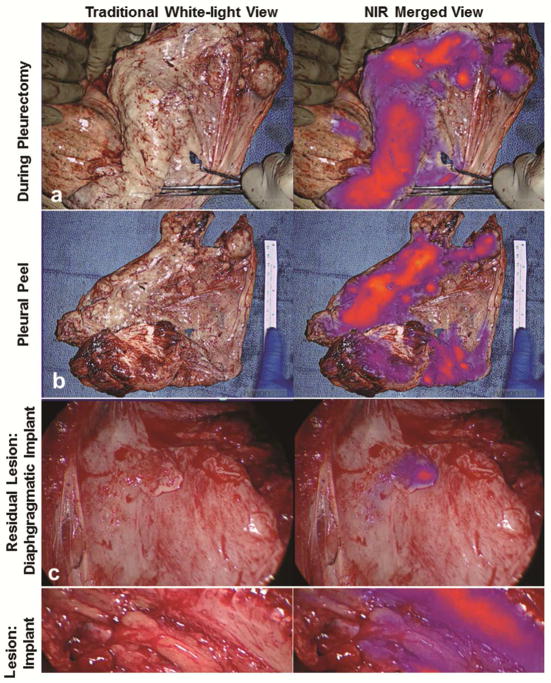
Figure 4.
FGS with ICG identifies occult macroscopic residual disease following complete resection. Following macroscopic resection using white-light only, the ipsilateral hemithorax was then evaluated in NIR imaging to determine if residual disease was present. Data from Subject 10 is used to illustrate the workflow. The surgeon first completed P/D (a). All resected specimens underwent ex vivo macroscopic fluorescence evaluation (b). Next, the chest was reevaluated with NIR imaging to assess for residual disease. An example of a diaphragmatic implant (c) and an intercostal lesion (d) are provided. Both lesions were MPM by histopathologic review.