Fig. 2.
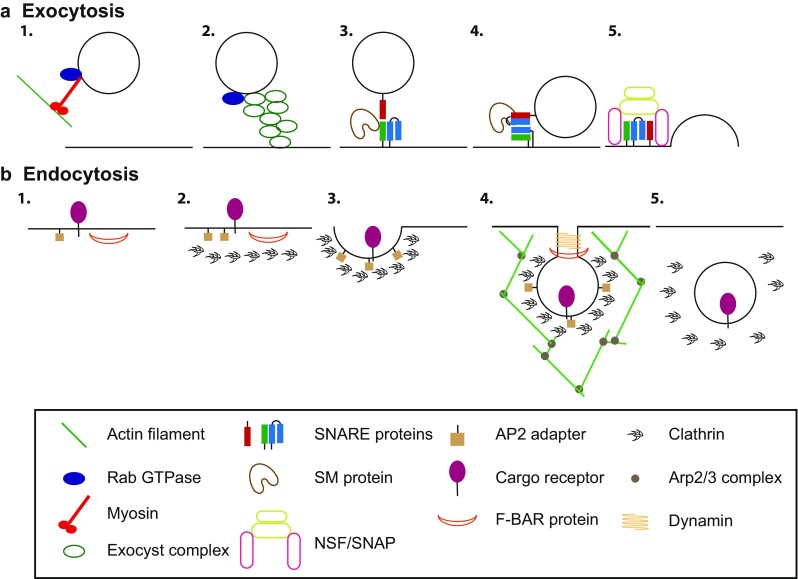
Illustration of exocytosis and endocytosis. a Exocytosis. (1) Vesicle delivery to the plasma membrane where it is (2) tethered by a tethering complex such as the exocyst, mediated by Rab GTPase. (3) SNARE proteins present on the vesicle and membrane are brought into proximity and (4) form a four helix bundle, templated by an SM protein. (5) SNARE complex formation drives fusion of vesicle to the plasma membrane, and NSF and SNAP proteins disassemble the cis SNARE complex. b Endocytosis. (1) Cargos and adaptor proteins on the membrane surface begin to cluster, (2) which recruits coat proteins such as clathrin. (3) The coat proteins promote membrane bending and invagination to form the endocytic pit. (4) Branched actin filaments are assembled and dynamin is recruited to the neck, with the help of F-BAR domain containing proteins, the vesicle is pinched off from the plasma membrane and is uncoated (5)
