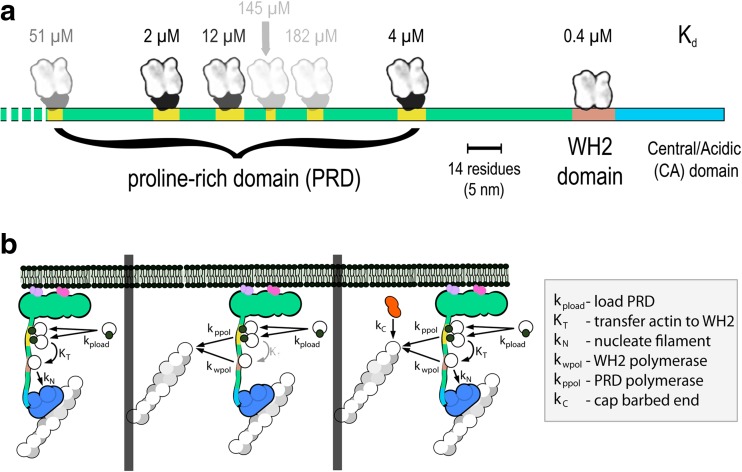
Fig. 3.
Layout of the WAVE1 PWCA domain and flux of actin and profilin-actin through the proline-rich and WH2 domains. a Linear model of the PWCA domain from WAVE1, consisting of amino acids 277–559. Profilin-binding sites in the proline-rich domain are marked in yellow, the actin-binding WH2 domain is red, and the central/acidic region is blue. Actin monomers and profilin-actin complexes are shown on the same scale as the linear extent of the PWCA polypeptide (note scale bar). The affinity (dissociation equilibrium constant) of each profilin or actin-binding site is marked above in micromolar. b Pathways by which actin flows through surface-associated WASP family proteins and into growing filament networks. Left: poly-proline sequences bind profilin-actin complexes and can transfer monomeric actin onto the WH2 domain. From there, the actin can be used to activate the Arp2/3 complex and create a new filament, branching from the side of a preexisting filament. Middle: Actin can be transferred from the WH2 domain and poly-proline sequences onto the ends of nearby filaments. Decreased transfer from the poly-proline sequences and increased depletion by nearby filaments decreases the occupancy of the WH2 domain and slows the rate of nucleation. Right: capping protein decreases the number of growing filaments and increases the steady-state occupancy of both the WH2 domain and the poly-proline sequences