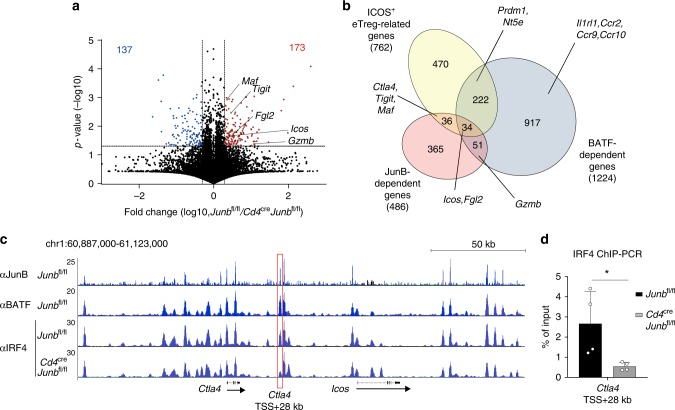
Fig. 6.
JunB diversifies targets for BATF and IRF4 in eTreg cells. a–c RNA-seq analysis of CD4+CD25+ Treg cells isolated from spleens of Cd4CreJunbfl/fl and Junbfl/fl mice. a Volcano plot comparing gene expression of Treg cells isolated from Cd4CreJunbfl/fl mice versus those from Junbfl/fl mice. b Venn diagram of genes upregulated by JunB (JunB-dependent genes) and BATF (BATF-dependent genes), and genes expressed in ICOS-expressing CD62Llo eTreg cells. c ChIP-seq analysis of CD4+CD25+ Treg cells isolated from spleens of Cd4CreJunbfl/fl and Junbfl/fl mice. Cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies in the presence of IL-2 for 60 h and used for ChIP-Seq analysis with antibodies against JunB, BATF, and IRF4. The genomic region containing Ctla4 and Icos genes was shown. The red box indicates a region located 28 kb downstream of transcription start site of Ctla4 (Ctla4 TSS + 28 kb) in which the level of IRF4-binding was significantly decreased by JunB deficiency. Arrows indicate the direction of gene transcription. d ChIP-PCR analysis of CD4+CD25+ Treg cells isolated from spleens of Cd4CreJunbfl/fl and Junbfl/fl mice. Cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies in the presence of IL-2 for 72 h and used for ChIP with anti-IRF4 antibody. Immunoprecipitated DNA was analyzed by qPCR using primers to detect the IRF4-binding site located in the Ctla4 TSS + 28 kb region. Error bars indicate s.d. (n = 4). *P < 0.05 (unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test). Data represent two independent experiments