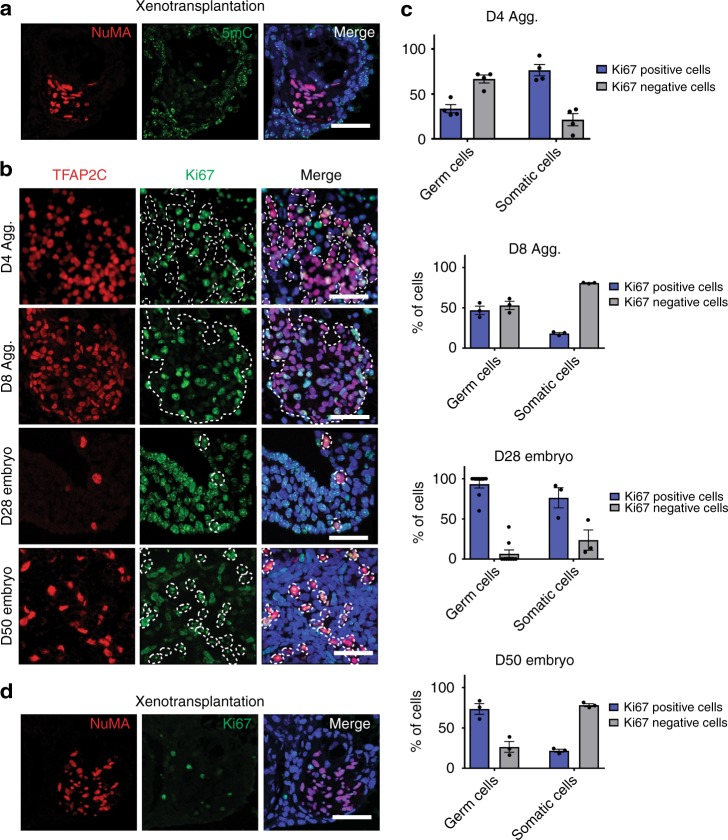
Fig. 5.
Xenotransplantation is associated with rPGCLCs epigenetic reprogramming and precocious exit from the cell cycle. a Donor cells are detected through their expression of the nuclear mitotic apparatus protein (NuMA, red) in paraffin sections of recipient testicles (n = 13) xenotransplanted with a single cell suspension of Day (D) D4 aggregate cells derived from riPSC90. 5mC (green) was detected in recipient somatic cells. Scale bar, 50 µm. b IF on paraffin sections of aggregates at D4 and D8, and rhesus embryos at CS12 (D28) and CS23 (D50) for the rPGCLC/rPGC marker TFAP2C (red) and the proliferation marker, Ki67(green). Nuclei were detected using DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 50 µm. c Quantification of Ki67 positive (blue bar graphs) and Ki67 negative (gray bar graphs) rPGCLCs/rPGCs and somatic cells in aggregates at D4 and D8, and rhesus embryos at CS12 (D28) and CS23 (D50). All data points used to generate bar graphs (black circles) were overlaid to the corresponding bar graphs, error bars represent the Standard Error of the Mean (S.E.M.), N = 3 technical replicates. d Recipient mouse testicles (n = 13) xenotransplanted with riPSC90 D4 aggregate cells co-stained for NuMA (red) and Ki67 (green). Nuclei were detected using DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 50 µm