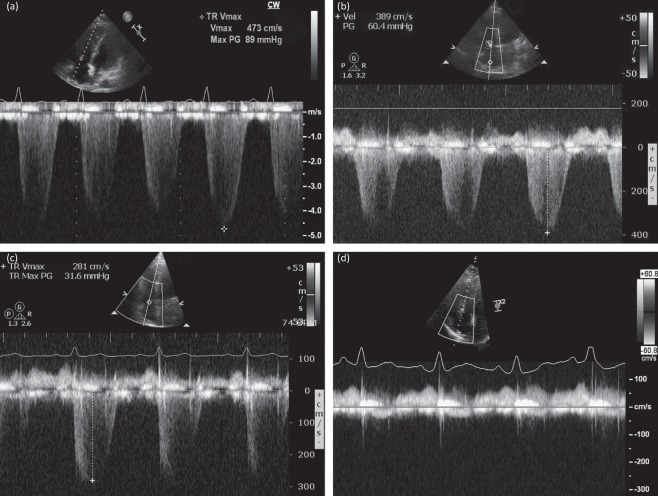
Fig 1.
Doppler echocardiographic recordings taken across the tricuspid valve, using the velocity of the tricuspid regurgitant (TR) jet to estimate right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP). On first presentation, a severely elevated RVSP of 89 mmHg + right atrial (RA) pressure was recorded (a). After 24 h of treatment, this improved to 60 mmHg + RA pressure (b). Before discharge from hospital, the RVSP had fallen further to 31 mmHg + RA pressure (c) and, when the patient was seen several months after discharge, there was no detectable TR jet and no evidence of pulmonary hypertension (d).