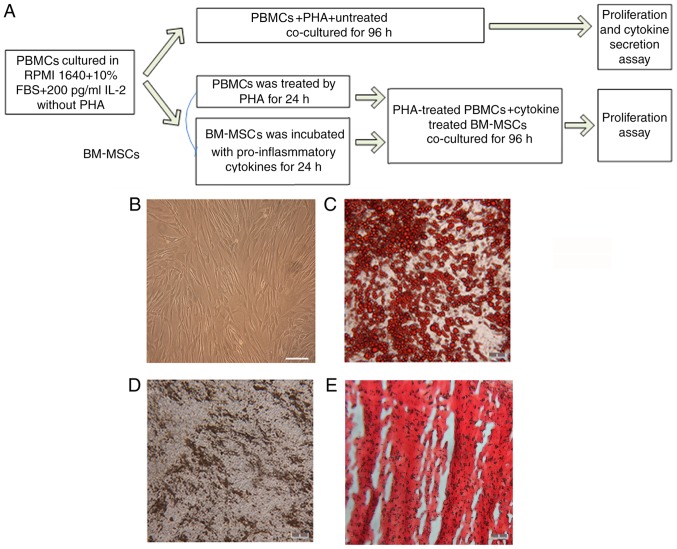
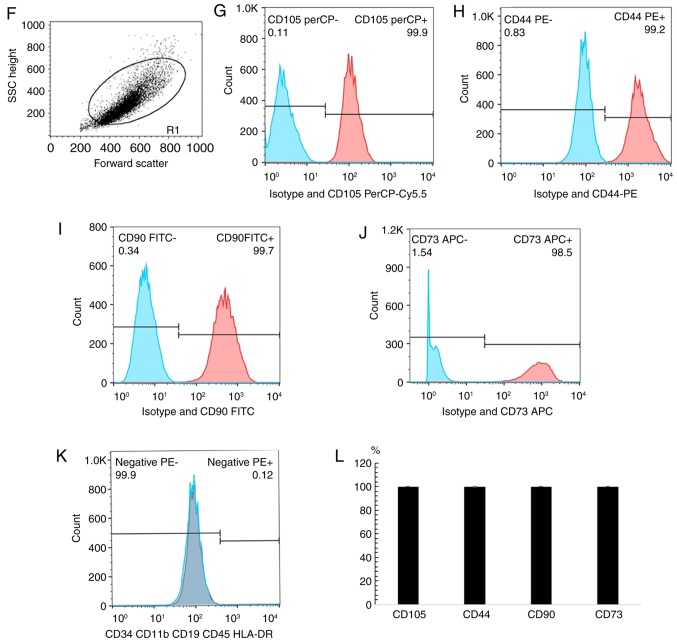
Figure 1.
Differentiation and cytometry characterization of cultured human BM-MSCs. (A) Schematic paradigm of the co-culture experiments. (B) Following 3–5 passages, the BM-MSCs exhibited spindle-like shape. (C) Formation of lipid vacuoles was detected by Oil Red O staining. (D) Osteogenesis was tested by von Kossa staining of the mineralized matrix. (E) Chondrogenesis was indicated by Safranin O staining. Scale bar, 100 µm. (F) The cells gated for analysis. With isotype control, cytometry tests identified that BM-MSCs at passage 3–5 were positive for (G) CD105 (H) CD44, (I) CD90 and (J) CD73, and negative for (K) CD34, CD11b, CD19, CD45 and HLA-DR. (L) The summary of quantified flow cytometry results as percentages. n=3. PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; PHA, phytohemagglutinin; BM-MSCs, bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells; CD, cluster of differentiation.