Figure 4.
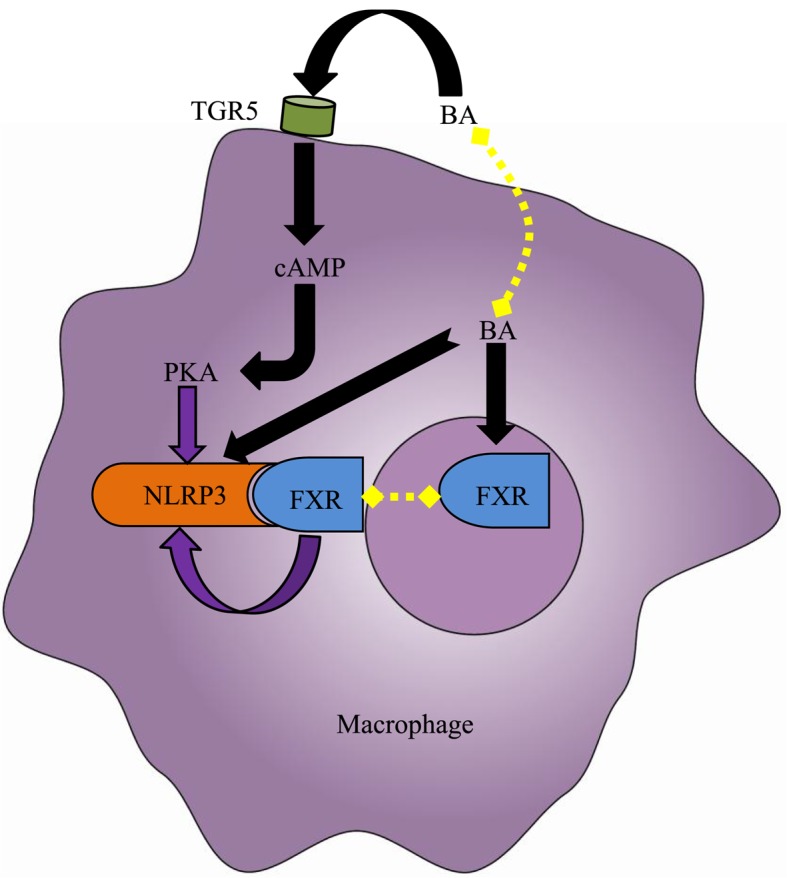
Effect of BA on the NLRP3 inflammasome in the macrophage. Elevated intracellular BAs, including deoxycholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid, directly activate the NLRP3 inflammasome in macrophages. However, the BA nuclear receptor FXR interacts with NLRP3 to prevent the assembly of NLRP3 inflammasome components, thereby repressing its activation. Furthermore, the BA membrane receptor TGR5 may negatively regulate NLRP3 inflammasome activation by TGR5-cAMP-PKA axis-dependent NLRP3 phosphorylation and ubiquitination. However, due to the limited expression of FXR and TGR5 under cholestasis conditions, the aforementioned protective mechanisms fail to counteract the cytotoxic effects of BAs. Black arrows indicate ‘promotion’, whereas, purple arrow indicates ‘inhibition’. BA, bile acid; cAMP, cylic adenosine monophosphate; FXR, farnesoid-X receptor; PKA, protein kinase A; TGR5, Takeda G-protein receptor 5; NLRP3, NACHT, LRR, and PYD domains-containing protein 3.
