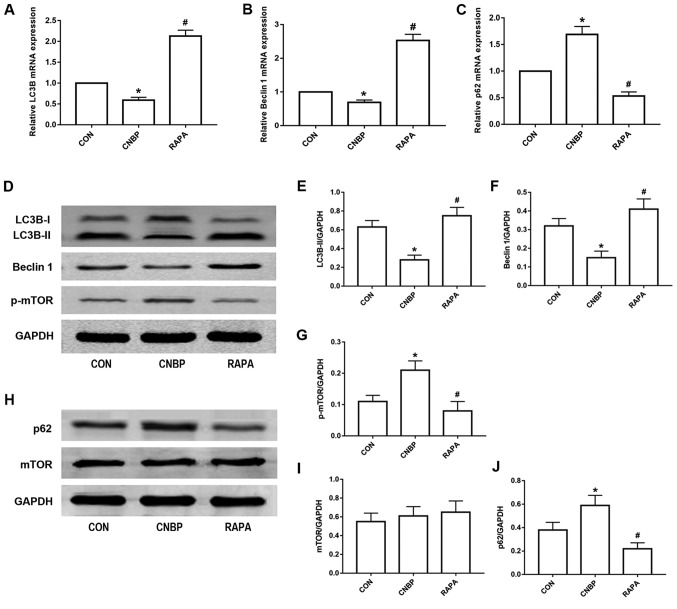
Figure 5.
Rapamycin treatment induces autophagy in rats via the inhibition of mTOR phosphorylation. The relative mRNA expression levels of (A) LC3B, (B) Beclin 1, and (C) p62, as measured by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis, in the prostates of rats from the three groups. (D) Representative western blot images of LC3B, Beclin 1 and p-mTOR from the three groups. Quantitative analysis was used to assess the levels of (E) LC3B-II, (F) Beclin 1, and (G) p-mTOR in the different groups. (H) Representative western blot images of p62 and mTOR from the three groups. Quantitative analysis was used to assess the expression levels of (I) p62 and (J) mTOR in the different groups. The values obtained were normalized against GAPDH. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. *P<0.05 vs. the CON group; #P<0.05 vs. the CNBP group. CON, control; CNBP, chronic non-bacterial prostatitis; RAPA, rapamycin; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; p-mTOR, phosphorylated mTOR; LC3B, microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3β.