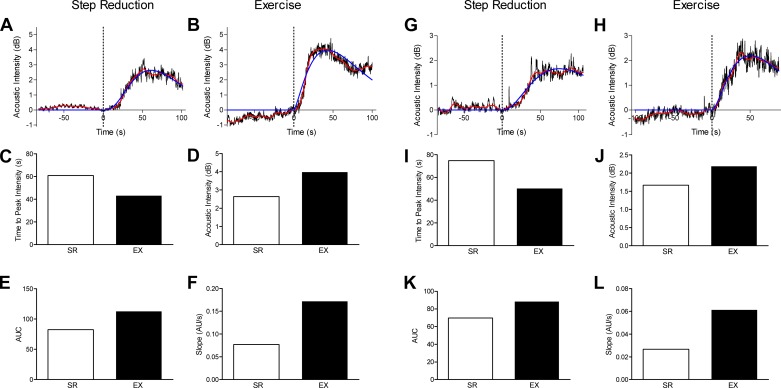
Fig. 3.
Representative examples of the application of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) to assess the effect of resistance exercise on the vastus lateralis in two healthy older men (65 and 69 yr old). Participants underwent a 14-day reduced-step count intervention combined with a unilateral leg resistance exercise protocol to assess whether resistance training performed during step reduction would prevent impairments to skeletal muscle microvascular perfusion. Unilateral leg resistance exercise, at 30% of one-repetition maximum, was performed every second day during the period of step reduction. After the 2-wk intervention, simultaneous assessment of resting vastus lateralis microvascular function was completed using CEUS in both the step-reduced (SR) and step-reduced plus exercise (EX) legs. Time-intensity curves were generated for each leg (A, B, G, and H), and measurements of time to peak intensity (C and I), acoustic intensity (D and J), area under the curve (AUC; E and K), and slope (F and L) were extracted from the gamma variate fit. AU, arbitrary units.