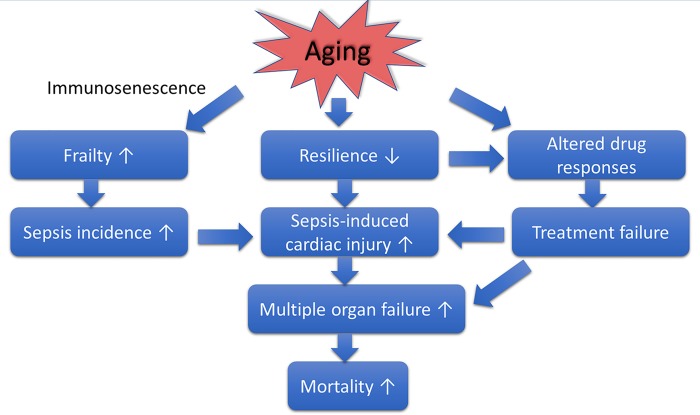
Fig. 1.
Scheme depicting the interaction between aging and sepsis-induced cardiac injury. Aging increases susceptibility to sepsis and results in a decreased resilience to sepsis-induced cardiac pathologies promoting multiple organ failure and increased mortality. The study of Inata et al. (3) adds to the growing evidence that aging also negatively impacts the effectivity of therapeutic interventions, which often leads to treatment failure.