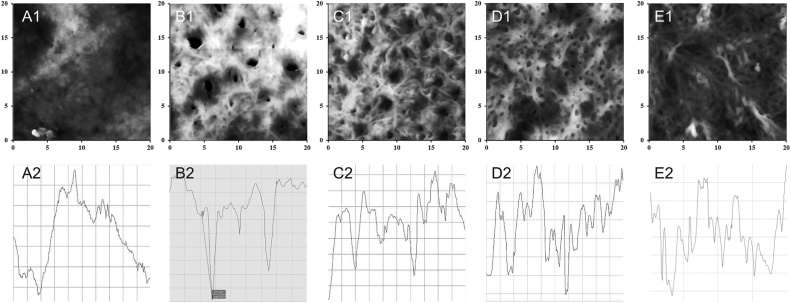
Fig. 1.
3-D Surface topography of biopolymer scaffolds. A – P(3HB) (scaffold 1); B – P(3HB/4HB) (scaffold 2); C – P(3HB/3 HV) (scaffold 3); D – P(3HB/3 HV/3HHx) 66.4/23.4/10.2 (scaffold 4); E – P(3HB/3 HV/4HB/3HHx) 63.5/19.4/12.3/4.8 (scaffold 5). A1-E1 – 3-D reconstructions of surface topography of scaffolds (surface areas 20 μm × 20 μm). A2-E2 – cross-sectional profiles of permanent topography of scaffolds. Abscissae axis is plane, 20 μm for all variants A2-E2. Ordinates axis is the relief depth for A2 – [50–350 nm]; B2 – [400–2400 nm]; C2 – [100–900 nm]; D2 – [400–1100 nm]; E2 – [300–1000 nm].