Fig. 6.
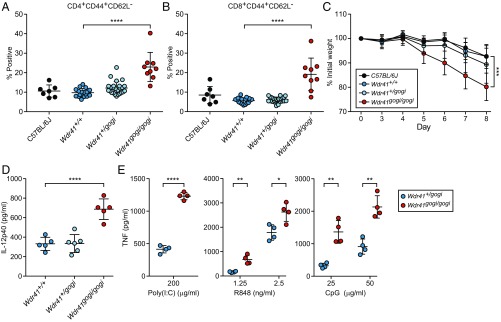
WDR41 deficiency phenocopies loss of SMCR8 function. (A and B) Frequency of CD44+CD62L− CD4+ (A) and CD8+ (B) T cells in peripheral blood from C57BL/6J mice (n = 7) and G3 mice from a single pedigree carrying the Wdr41gogi allele [Wdr41+/+ (n = 17), Wdr41+/gogi (n = 25), and Wdr41gogi/gogi (n = 9)]. (C) Weight loss analysis of C57BL/6J (n = 10), Wdr41+/+ (n = 7), Wdr41+/gogi (n = 14), and Wdr41gogi/gogi (n = 6) treated with 1.4% DSS. (D) Plasma levels of IL-12p40 detected in untreated 6-mo-old gogi mice [Wdr41+/+ (n = 5), Wdr41+/gogi (n = 5), and Wdr41gogi/gogi (n = 5)]. (E) ELISA analysis of TNF secretion by peritoneal macrophages (n = 4 mice per genotype) stimulated for 6 h with indicated concentrations of poly(I:C), R848, and CpG. In A, B, D, and E, data points represent individual mice. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Data are expressed as means ± SD, and the significance of differences between genotypes was determined by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons (A–D) or unpaired Student’s t test (E) (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001). For C, the statistical assessment for the last time point is indicated.