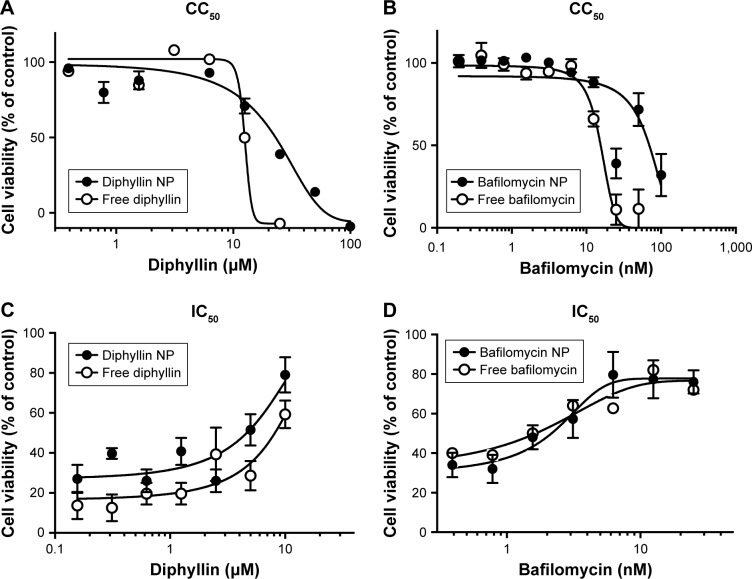
Figure 4.
CC50 and IC50 of free and nanoparticulate V-ATPase inhibitors.
Notes: (A) Free diphyllin or diphyllin NP was added to MH-S cells and incubated for 72 hours. An alamarBlue assay was performed and cell viability was normalized to the value of untreated medium controls (100%). (B) Free bafilomycin or bafilomycin nanoparticles (bafilomycin NP) were added to MH-S cells and incubated for 72 hours. An alamarBlue assay was performed and cell viability was normalized to the value of untreated medium controls (100%). (C) Free diphyllin or diphyllin NP was added to MH-S cells and incubated for 1 hour. Cells were then infected with influenza virus H1N1 at an MOI of 1 for another hour. Viruses were removed and the free diphyllin or diphyllin NP was added back to the cells. Twenty-four hours later, cellular viability was examined by an alamarBlue assay, and cell viability was normalized to the value of uninfected cell controls (100%). (D) Free bafilomycin or bafilomycin NP was added to MH-S cells and incubated for 1 hour. Cells were then infected with influenza virus H1N1 at an MOI of 1 for another hour. Viruses were removed and the free bafilomycin or bafilomycin NP was added back to the cells. Twenty-four hours later, cellular viability was examined by an alamarBlue assay, and cell viability was normalized to the value of uninfected cell controls (100%). Data in the plot represent mean ± SEM out of four test replicates.
Abbreviations: CC50, 50% cytotoxic concentration; IC50, 50% inhibitory concentration; V-ATPase, vacuolar ATPase; NP, nanoparticle; MOI, multiplicity of infection; SEM, standard error of the mean.