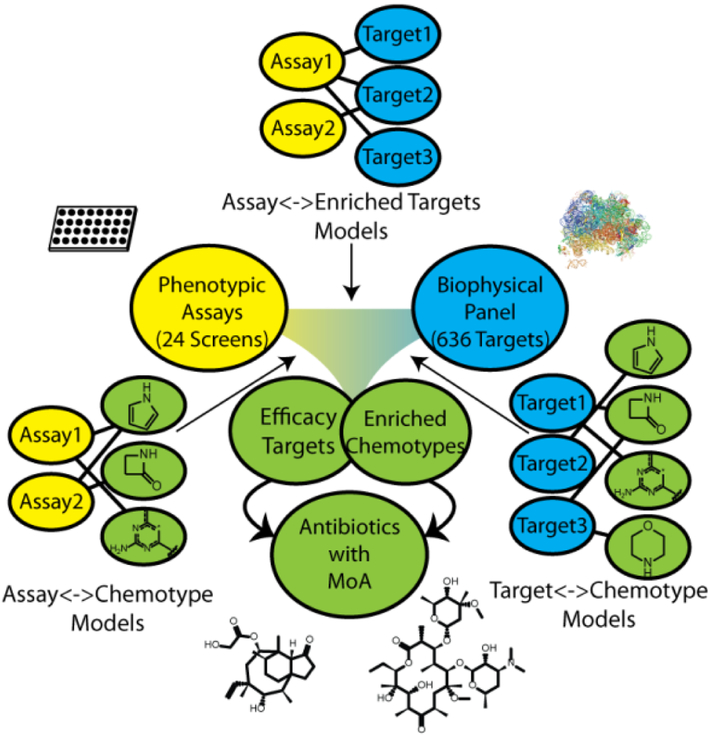
Figure 1:
Overview of our cheminformatic approach to mechanism of action prediction for antimicrobial drug discovery. Naïve Bayes models were generated for a series of phenotypic and biophysical binding screens using a joint Enriched Antibacterial training set of ~55,000 compounds (see Methods). Models identified protein targets that were enriched in phenotypic assays (binders of that target were enriched as phenotypic actives). Models linking a phenotypic screen and enriched target of interest to chemical matter identified chemotypes enriched for both binding to the target and phenotypic screen activity (bacterial killing). Compounds possessing the selected chemotypes were hypothesized to achieve efficacy in killing bacteria by acting through the enriched efficacy target.