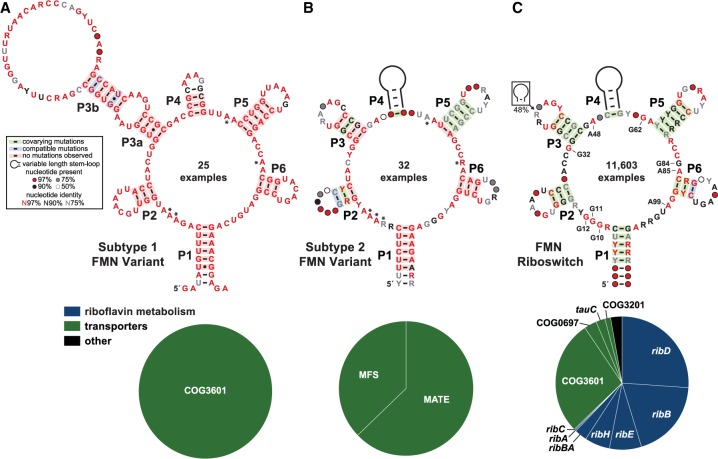
FIGURE 1.
Variant FMN motif RNAs differ from the FMN riboswitch consensus and its typical genetic associations. (A) Consensus sequence and secondary structure model of 25 unique examples of subtype 1 variant FMN RNAs. Asterisks identify key nucleotides that differ from FMN riboswitch consensus. The key (box) describes the annotations in the consensus models. (Bottom) Pie chart of the genes located immediately downstream from subtype 1 RNAs. (B) Consensus model and gene associations for 32 unique examples of subtype 2 RNAs. Additional annotations are as described for A. (C) Consensus model and gene associations for 11,603 unique examples of FMN riboswitch aptamers. Certain nucleotides that are most directly involved in forming the ligand binding pocket for FMN are numbered according to the crystal structure model (PDB ID code 3F2Q) published previously (Serganov et al. 2009).