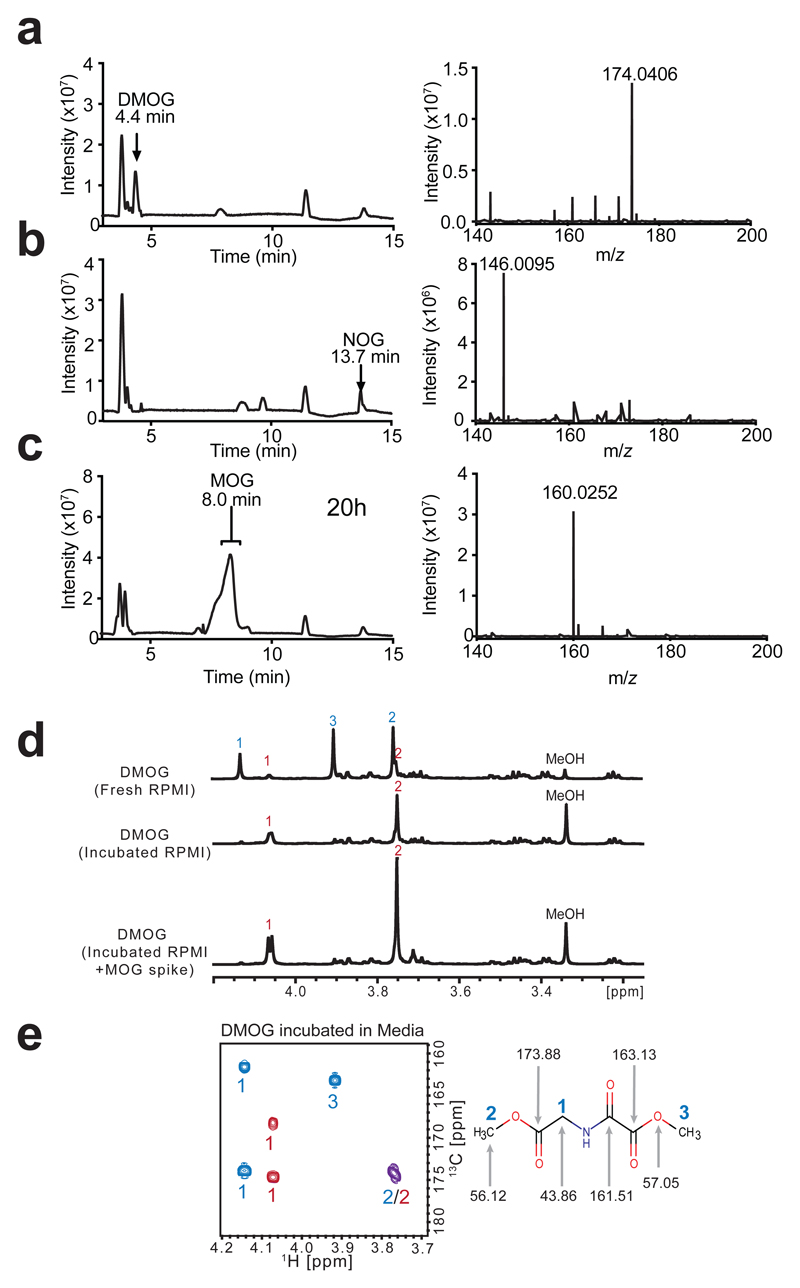
Figure 2. The methyl oxoacetate ester of DMOG is rapidly hydrolysed in cell culture media to yield MOG.
a) LC-MS base-peak chromatogram and corresponding mass spectrum of 10 µM DMOG in water, with peak and ion annotated.
b) LC-MS base-peak chromatogram and corresponding mass spectrum of 10 µM NOG in water, with peak and ion annotated.
c) LC-MS base-peak chromatogram demonstrating the MOG peak formed after incubation in water for 20 h at room temperature. Right: mass spectrum of MOG peak, with ion corresponding to MOG annotated.
d) 1D-1H-NMR spectra of DMOG freshly resuspended in RPMI medium, or after incubation in RPMI medium overnight, with and without the addition of a synthesised MOG standard. Signals annotated according to the labelled structure of DMOG in (e), DMOG peaks with blue numbers and MOG peaks with red numbers.
e) 2D-1H,13C-HMBC-NMR spectrum of DMOG incubated in RPMI media, DMOG peaks with blue numbers and MOG peaks with red numbers, overlapping cross-peak shown in purple. Right: DMOG structure annotated with the relevant 13C signal shifts.
Data are representative of more than 3 independent experiments each with similar results.