Figure 4. Microscopic Anatomy of Pulmonary Lymphatics and Translocation of Fibers to the Pleural Space.
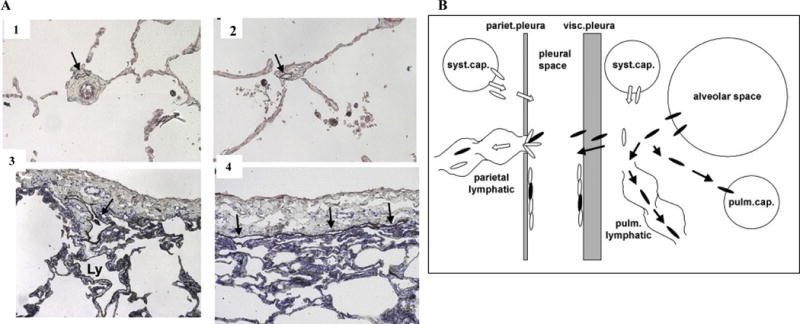
A. alveoli (panel A2). Lymphatics of the interlobular septa (Ly in panel A3) drain into lymphatics beneath the visceral pleura (arrows in panels A3, 4). Immunohistochemical detection of lymphatics with toluidine blue counterstain, original magnification × 10 (Sozio et al., 2012). Reprinted with permission from John Wiley and Sons.
B. Miserocchi et al. (2008) hypothesize that asbestos-induced pulmonary inflammation increases interstitial fluid pressure that allows biopersistent fibers to penetrate into pulmonary lymphatics and cross the visceral pleura. Fibers that are not cleared through lymphatic stomata are trapped at the parietal pleura leading to the development of mesothelioma as proposed in Figure 2. Reprinted with permission from an Open Access article (Miserocchi et al., 2008).
