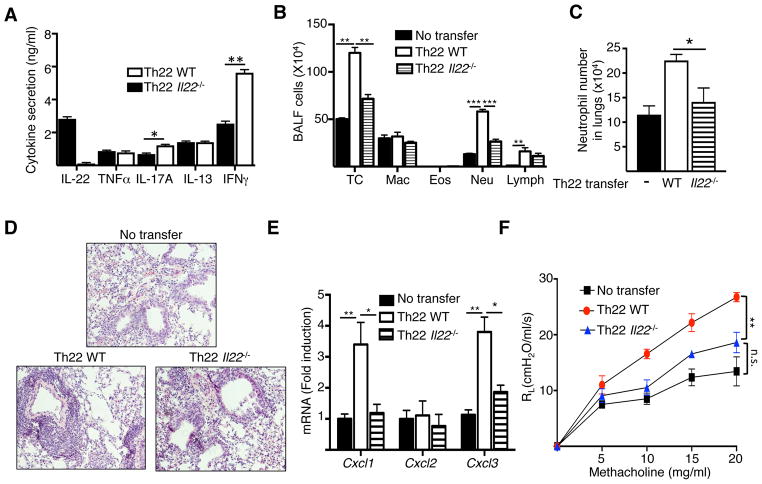
Figure 5. Th22 antigen-specific CD4+ T cells drive neutrophil-dominated airway inflammation and AHR in response to intranasal antigen challenge.
A. Cytokine secretion by vitro polarized Th22 cells from in WT and Il22−/− mice. B-F. Total and differential cell counts in BALF (B), frequency of neutrophils in lungs (C), H&E stained lung sections (D), chemokine mRNA levels in lungs (F), and lung resistance in response to increasing doses of methacholine (G) in WT recipients of Th22 polarized OVA-specific CD4+ T cells from DO11.10 and DO11.10/Il22−/− mice following n. challenge with OVA. Mice that received no T cells were used as controls. Bars represent mean±SEM (n=4–6 per group). *p<0.05, **p<0.05, ***p<0.001.